A Journey Through Time: Mapping Ancient Rome and Jerusalem
For centuries, Rome and Jerusalem have captivated historians and travelers alike. These two powerful cities, though geographically distant, were intertwined throughout much of their ancient history. But how close were they? Let's explore maps depicting these ancient cities and their respective empires.
The Mediterranean World: A Roman Sea
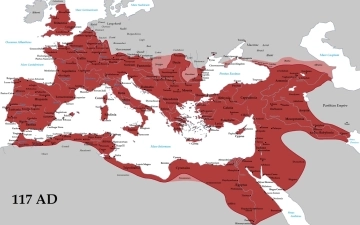
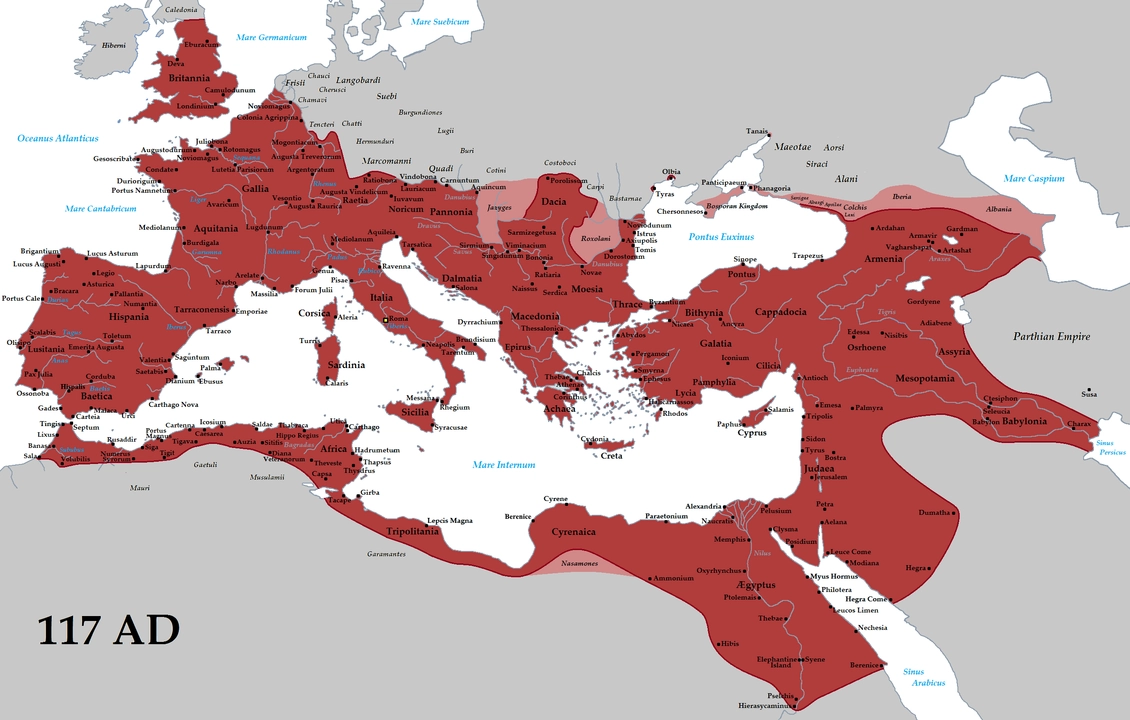
During the height of the Roman Empire, the Mediterranean Sea served as a vital trade route. A map of the Roman Empire at its greatest extent (roughly 1st-2nd centuries CE) would show Rome at the center, with its dominion stretching across Europe, North Africa, and parts of the Middle East. Jerusalem would be a speck within the Roman province of Judea.
A Closer Look: Judea Under Roman Rule
Zooming in on the eastern Mediterranean, a map of Judea during the Roman era (1st century BCE to 4th century CE) would depict Jerusalem as the political and religious center of the region. Roman roads connected Jerusalem to other major cities within the province, facilitating trade and troop movement.
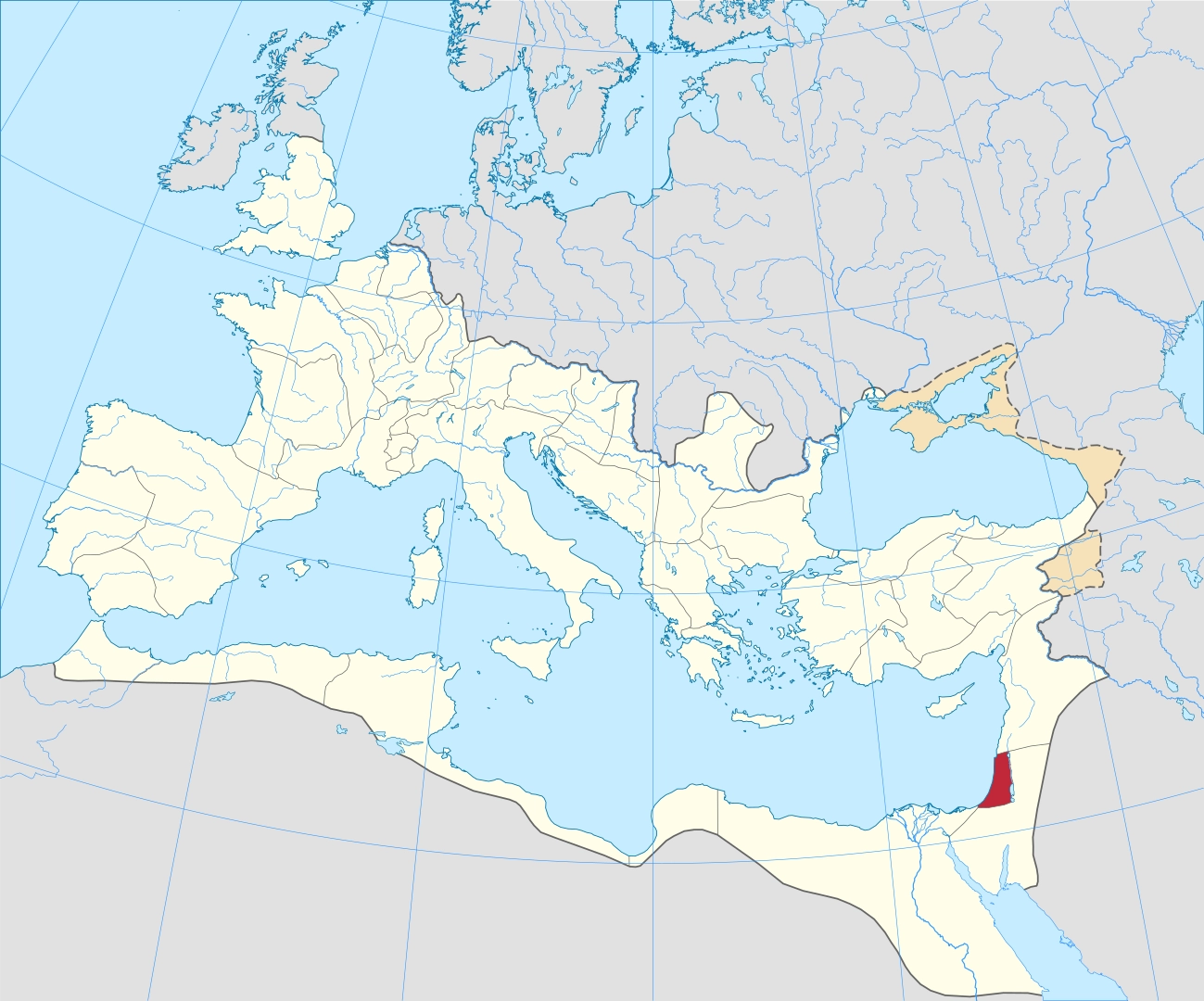
Separate Cities, Shared History
While Rome and Jerusalem weren't exactly neighbors, their paths crossed in significant ways. The Roman conquest of Judea in 63 BCE significantly altered Jerusalem's history. Roman administration, architecture, and culture all left their mark on the city. The destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem by the Romans in 70 CE stands as a defining moment in Jewish history.
Exploring the Past: Resources for Further Discovery
For history buffs interested in a deeper dive, numerous resources are available online and in libraries. The Peutinger Map, a Roman roadmap dating back to the 3rd or 4th century CE, offers a fascinating glimpse into the ancient world, though Jerusalem itself is not depicted.
Additionally, archaeological excavations in both Rome and Jerusalem continue to unearth new artifacts and shed light on the lives of those who inhabited these ancient cities.
Whether you're a history buff or simply curious about the connections between different cultures, exploring maps of ancient Rome and Jerusalem offers a glimpse into a world where empires rose and fell, leaving behind a rich legacy that continues to resonate today.
Related Posts
A Journey Through Time: Mapping Ancient Rome and Jerusalem
For centuries, Rome and Jerusalem have captivated historians and travelers alike. These two powerful cities, though geographically distant, were intertwined throughout much of their ancient history. But how close were they? Let's explore maps depicting these ancient cities and their respective empires. The Mediterranean World: A Roman Sea During the height of...
Read MoreThe Role of Horses in the Roman Empire: From War to Sport
If we look back on the Roman Empire, we can see that horses played an important role. They were engines of power and symbols of prestige, and they were used for agriculture, traveling, warfare, and yes, entertainment like chariot races. Spanning centuries of conquest and culture, horses have always been closely...
Read MoreSeverus Alexander: The Emperor Who Faced Down Crisis and Attempted to Restore Order
Severus Alexander, often overshadowed by the more flamboyant and controversial emperors who preceded him, was a ruler who ascended to the imperial throne at a time of profound crisis. His reign, while ultimately brief, was marked by a determined effort to restore order and stability to the Roman Empire. Grandson of...
Read MoreDrive the Magic: Why Renting a Car in Miami is the Key to Unlocking the Best of the City
Miami isn’t just a city—it’s a vibe. With its sun-drenched beaches, pulsing nightlife, exotic cuisine, and vibrant cultural districts, it’s a place that begs to be explored. But here’s the truth: Miami wasn’t made to be experienced from the back seat of a cab or behind the window of a...
Read MoreLeadership and Planning Skills That Help with Moving
Relocating to a new home or city can be one of life's most stressful events. It involves juggling logistics, coordinating multiple people, and making critical decisions, all while managing the emotional toll of change. But if you approach your move with strong leadership and effective planning skills, the process becomes...
Read MoreMarcus Aurelius: Philosophy and Leadership in the Midst of Turmoil
In the annals of Roman history, the name Marcus Aurelius stands as a symbol of wisdom, Stoic philosophy, and leadership during times of great adversity. His reign as Emperor from 161 to 180 CE coincided with challenging periods for the Roman Empire, including external threats and internal strife. In this...
Read More