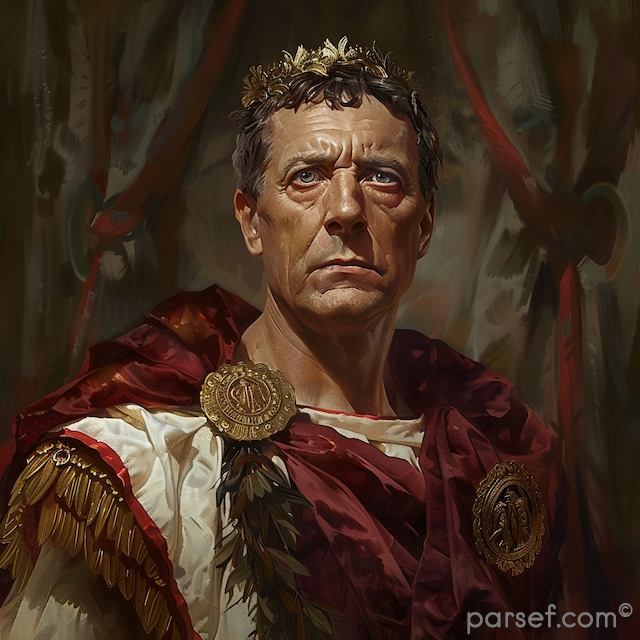
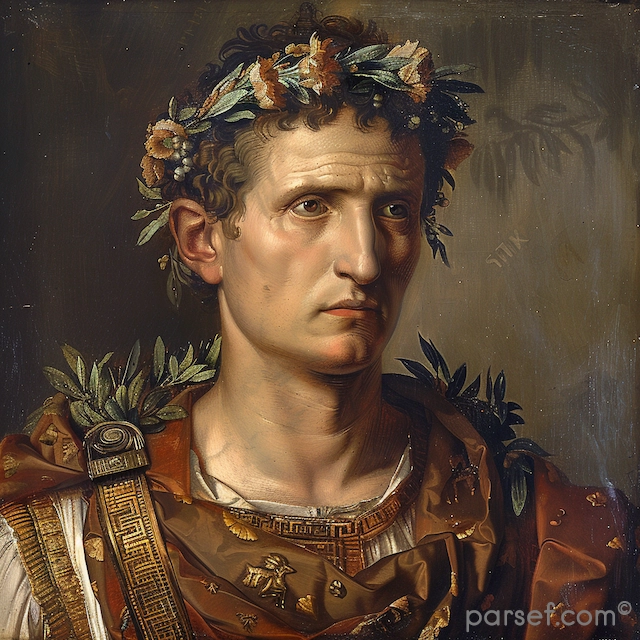
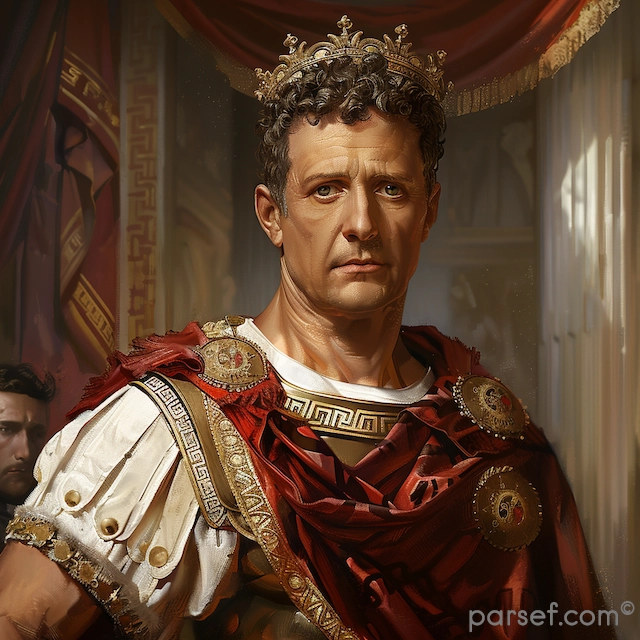
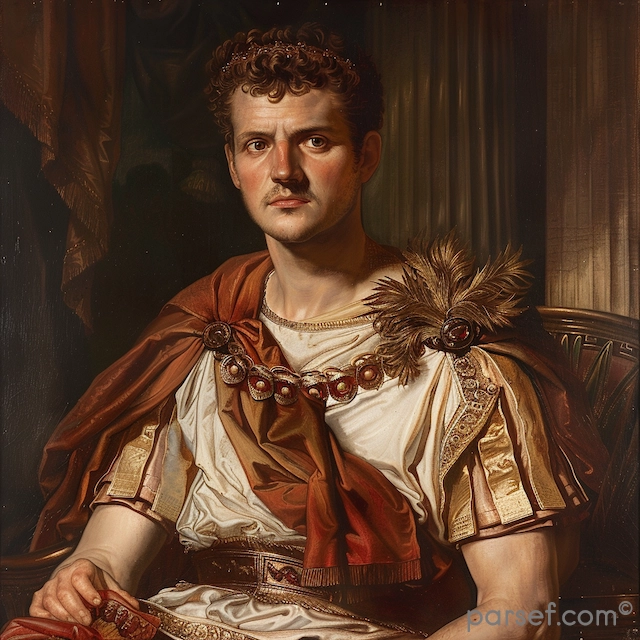
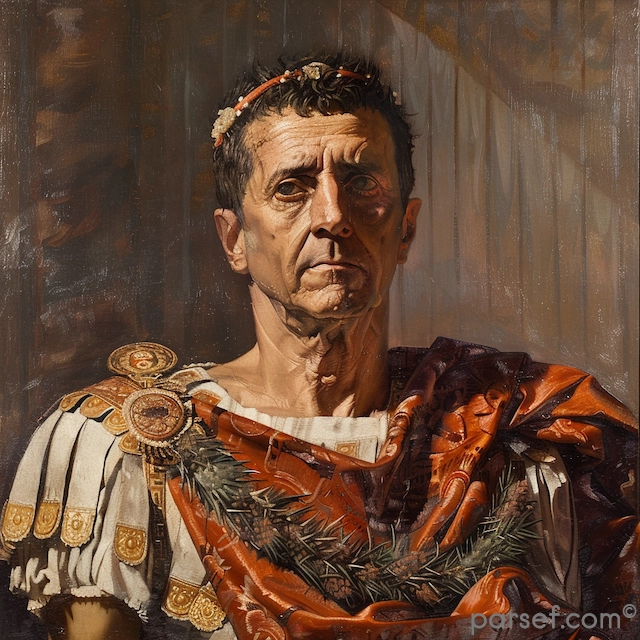
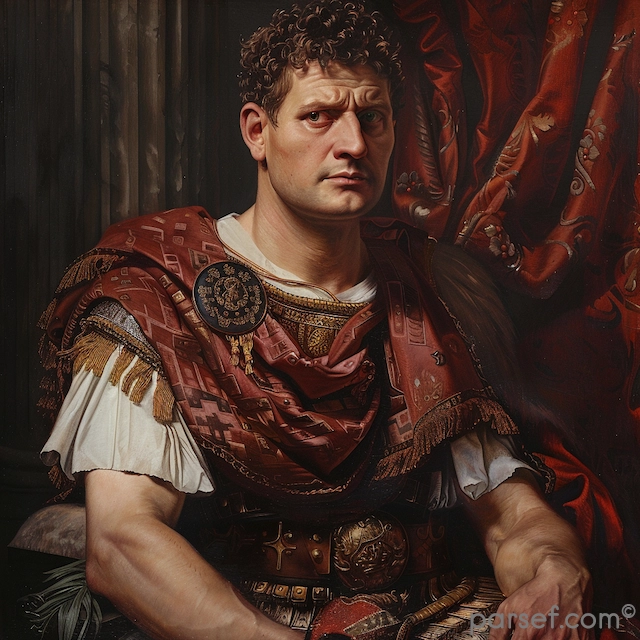
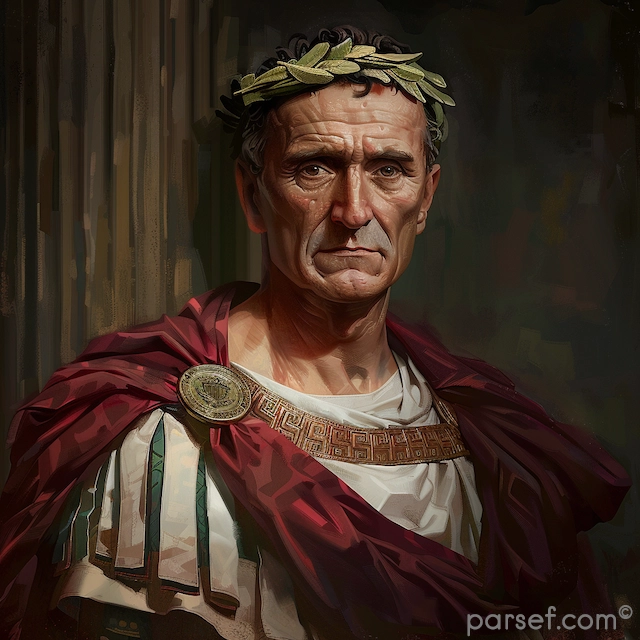
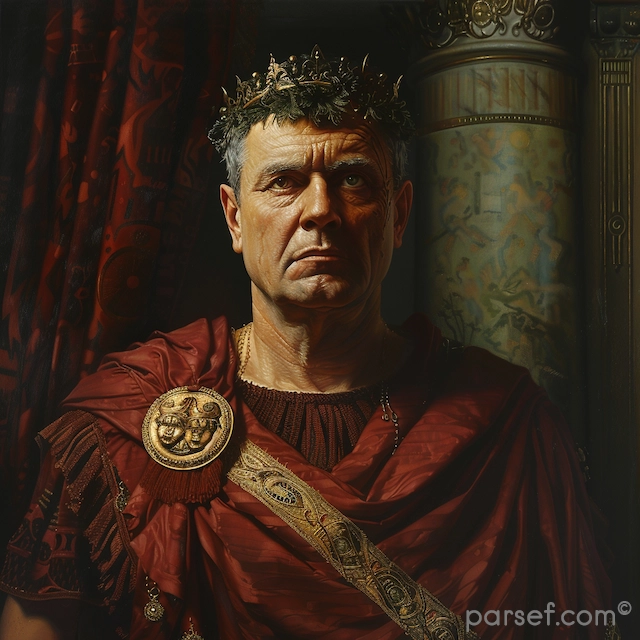
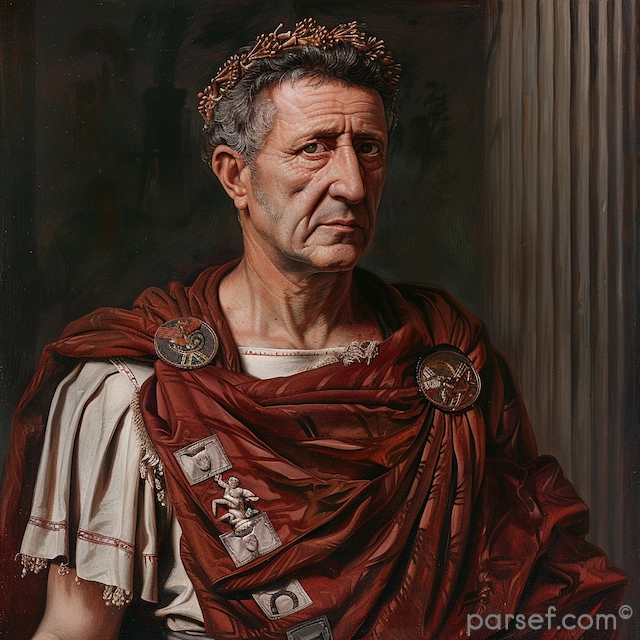
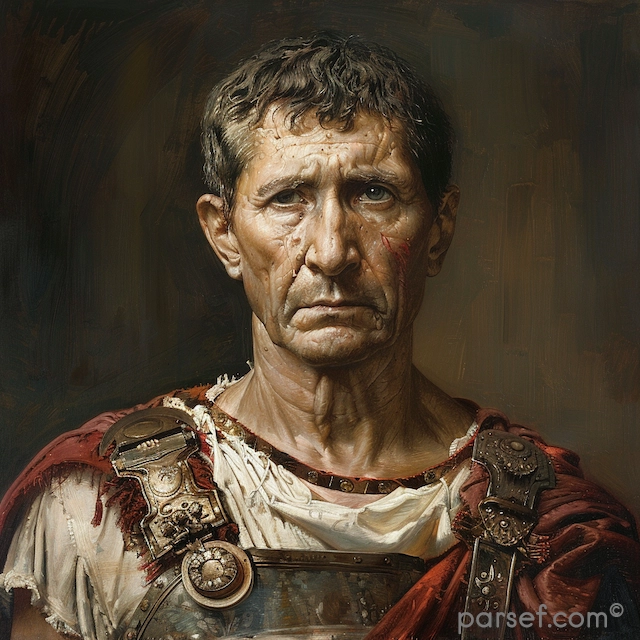
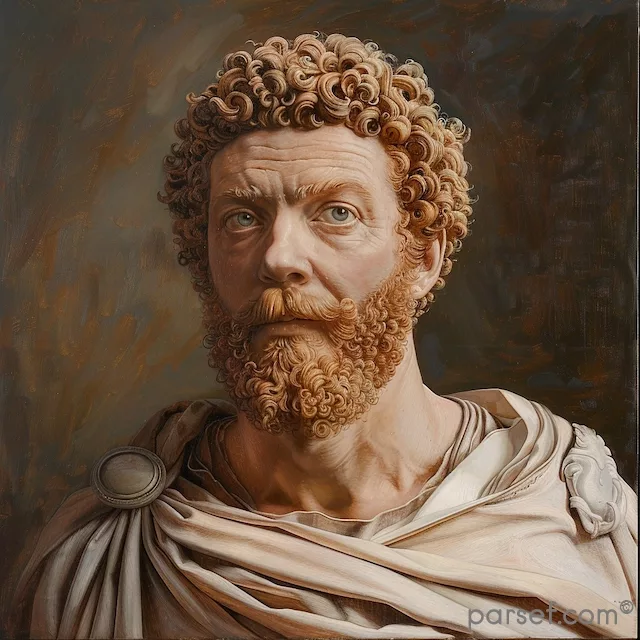
Caracalla: The Emperor of Bloodshed and the Architect of Roman Citizenship
Caracalla, son of the formidable Emperor Septimius Severus, is a complex and contradictory figure in Roman history. Often remembered for his brutality and paranoia, he is equally renowned for one of the most far-reaching edicts in Roman law.
His reign was marked by a tumultuous blend of violence and reform. Shortly after ascending to power alongside his brother Geta, Caracalla engineered the assassination of his co-emperor. This fratricide, a shocking act even by Roman standards, plunged the empire into a period of fear and uncertainty. Caracalla’s paranoia grew, leading to a reign of terror marked by purges of potential rivals and the execution of countless innocent people.
Yet, amidst the blood and brutality, Caracalla also left a significant and enduring legacy. His most famous edict, the Constitutio Antoniniana, granted Roman citizenship to all free-born inhabitants of the Roman Empire. This sweeping reform had profound implications for the empire. It unified the legal system, extended Roman law to all citizens, and increased tax revenues. While motivated in part by a desire to increase tax income, the edict also represented a significant step towards the creation of a more unified Roman world.
Caracalla was also a patron of the arts and architecture. His most famous building project, the Baths of Caracalla, remains one of Rome's most impressive ancient ruins. These public baths were a testament to Roman engineering and a symbol of the empire's opulence.
However, the extravagance and brutality of Caracalla's reign ultimately undermined his authority. His assassination in 217 AD brought an end to his tumultuous rule. Despite his short life, Caracalla left an indelible mark on the Roman Empire. His legacy is a complex one, a blend of cruelty, reform, and extravagance.
Caracalla's reign serves as a stark reminder of the complexities of power and the human capacity for both great cruelty and great vision. His life and death offer a fascinating glimpse into the turbulent world of Roman imperial politics.
Related Posts
Roman Festivals and Public Holidays
In ancient Rome, festivals and holidays were important days for the people to come together and perform religious rituals. Since the Roman calendar didn’t have weekends, these feriae (holidays) would provide days of rest from people’s regular routine. There were three kinds of Roman holidays: Conceptivae: These annual holidays had...
Read MoreHow Online Tutoring Builds Stronger Foundations in Chemistry
Understanding chemistry often feels like learning a new language—symbols, equations, and reactions that demand more than just memorization. This is where online tutoring steps in as a game-changer. By offering personalized attention, real-time feedback, and flexible pacing, online tutoring helps students grasp core principles with confidence. It transforms abstract chemical...
Read MoreTrajan: Expanding the Roman Empire to Its Zenith
The Roman Empire, at its zenith, was a sprawling realm that stretched from Britannia in the north to Egypt in the south, and from Hispania in the west to Mesopotamia in the east. Among the emperors who played a pivotal role in this expansion and solidified Rome's dominance was Trajan....
Read MoreThe Perfect French Riviera Wedding
The French Riviera: A Timeless Wedding Destination The French Riviera, or Côte d’Azur, is one of the world’s most iconic destinations for weddings, offering breathtaking coastlines, luxurious estates, and a romantic Mediterranean backdrop. But beyond its modern allure, this glamorous stretch of land has a deep-rooted history that dates back to...
Read MoreOrganizing Archival Gear for Museums and Collectors
Proper archival care of equipment is necessary for collectors and museums to conserve valuable artifacts and records. Proper categorization, storage, and environmental control help maintain collections whole and durable. The implementation of proper archival care practices ensures historical materials are preserved and can be made accessible to future generations. Historical Note: preservation...
Read MoreBoost Productivity Respectfully: Non-Intrusive Alternatives to Screen Capture Monitoring
Screen monitoring has become essential in modern work environments, particularly with the shift towards remote and hybrid models. Many companies utilize screen capture tools to ensure productivity. But is this the best way to enhance employee performance? Overview of screenshot-based monitoring Screen capture employee monitoring is a popular tool used by managers...
Read More