Marcus Aurelius: Philosophy and Leadership in the Midst of Turmoil
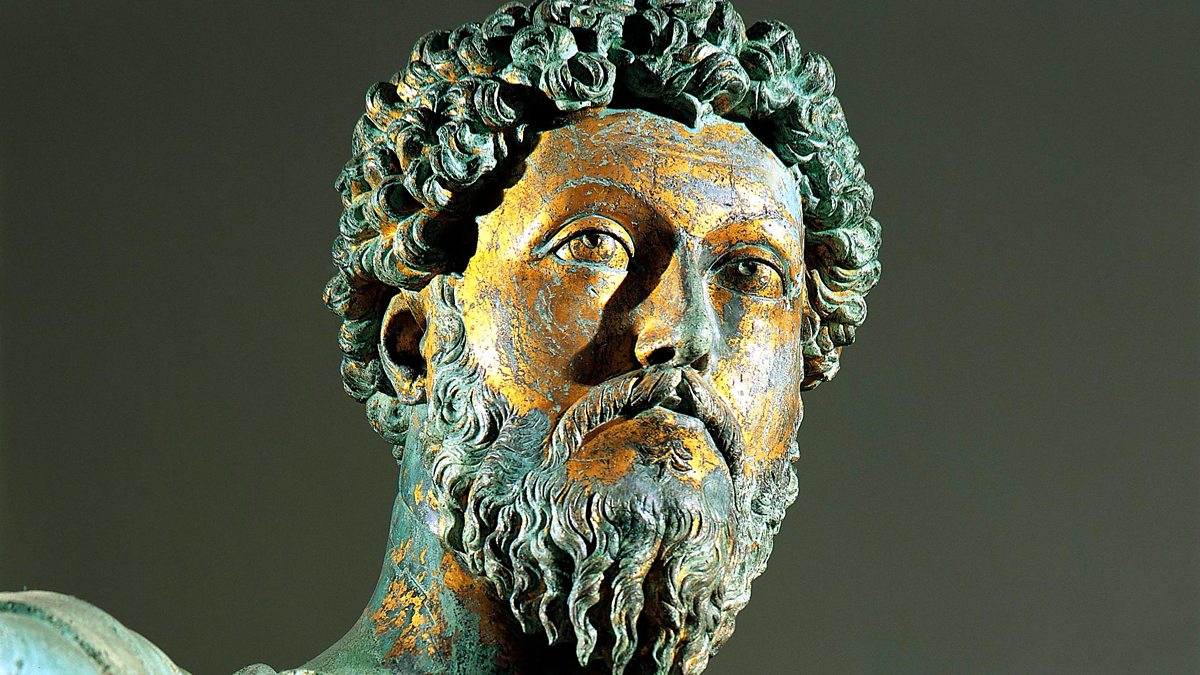

In the annals of Roman history, the name Marcus Aurelius stands as a symbol of wisdom, Stoic philosophy, and leadership during times of great adversity. His reign as Emperor from 161 to 180 CE coincided with challenging periods for the Roman Empire, including external threats and internal strife. In this article, we delve into the life and reign of Marcus Aurelius, exploring how his philosophical beliefs shaped his leadership during tumultuous times.
Early Life and Education
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus was born in 121 CE into a prominent Roman family. From a young age, he received a comprehensive education in literature, philosophy, and rhetoric. His early studies in Stoicism, a school of philosophy that emphasizes virtue, self-control, and rationality, would profoundly influence his life and reign.
The Five Good Emperors
Marcus Aurelius is often counted among the "Five Good Emperors," a period of relative stability and prosperity in the Roman Empire. His accession to the throne in 161 CE was marked by a shared rule with Lucius Verus. However, his co-emperor's early death placed the full burden of leadership on Marcus Aurelius' shoulders.
Stoicism and Leadership
Marcus Aurelius' reign was marked by his commitment to Stoic philosophy, which provided him with a moral and ethical framework for leadership. He believed in the importance of duty and virtue, emphasizing the well-being of his subjects above personal gain.
During his rule, the Roman Empire faced numerous challenges, including the Parthian War, the Antonine Plague, and invasions by Germanic tribes. Marcus Aurelius maintained a Stoic composure, often recording his thoughts in a series of personal writings known as the "Meditations." These writings provide insights into his philosophical outlook and his commitment to rational decision-making in the face of adversity.
Philosophy and Personal Ethics
In the "Meditations," Marcus Aurelius reflects on Stoic principles such as self-discipline, resilience, and the importance of distinguishing between what can be controlled and what cannot. He emphasizes the impermanence of life and the value of living in accordance with reason and virtue.
Legacy and Influence
Marcus Aurelius died in 180 CE, leaving behind a legacy as one of Rome's most respected emperors. His Stoic philosophy and ethical leadership continue to inspire leaders, philosophers, and individuals seeking guidance in facing life's challenges.
His writings in the "Meditations" have been translated and studied for centuries, offering timeless wisdom on topics ranging from personal ethics to leadership principles. Today, Marcus Aurelius is celebrated not only as a wise emperor but also as a philosopher-king whose enduring influence extends far beyond the boundaries of the Roman Empire.
Marcus Aurelius' reign serves as a testament to the power of philosophy in guiding leadership and personal conduct. His steadfast commitment to Stoic principles in the midst of turmoil showcases the enduring relevance of ancient wisdom in navigating the complexities of life and leadership.
Related Posts
Nero: The Notorious Emperor Who Fiddled While Rome Burned
The name Nero is synonymous with tyranny, extravagance, and the infamous image of an emperor who, according to legend, played the fiddle while Rome was engulfed in flames. Nero's reign is a dark chapter in the history of the Roman Empire, marked by cruelty, decadence, and the disastrous Great Fire...
Read MoreFrom Scrolls to Stones: How Museums Document Biblical History
The Bible is more than just a collection of sacred texts—it’s a living document that has shaped centuries of religious, cultural, and historical movements. For thousands of years, it has been passed down through oral traditions, written manuscripts, and monumental inscriptions. The story of how these texts came to be,...
Read MorePertinax: The Brief Respite in Rome’s Chaotic Succession Crisis
The latter part of the 2nd century AD was a period of profound instability for the Roman Empire. The capricious and tyrannical reign of Commodus had left the empire in a state of disarray. His assassination in 192 CE ushered in a chaotic period often referred to as the Year...
Read MoreThe Evolution of Customer Expectations In A Digital-First World
Introduction: When Everything Changed for Travelers Think back to your last vacation ten years ago. Going off-grid was actually part of the appeal, wasn't it? Fast forward to today, and that mindset seems downright prehistoric. Modern travelers want their phones working before the plane wheels touch down, and they're definitely not...
Read MoreThe Colossal Footprint: Exploring the Roman Empire at its Greatest Extent
The Roman Empire, a name that evokes images of gladiatorial combat, sprawling aqueducts, and stoic emperors, wasn't just a powerful state; it was a colossal empire that stretched across continents. But how vast was its reach at its zenith? This post delves into the greatest extent of the Roman Empire,...
Read MoreElagabalus: The Controversial Reign of Rome’s Youngest Emperor and His Religious Revolution
Elagabalus, born Varius Avitus Bassianus, is one of the most enigmatic and controversial figures in Roman history. Elevated to the imperial throne at the tender age of fourteen, his reign was marked by extravagance, scandal, and a radical religious transformation. His rise to power was as dramatic as his subsequent reign....
Read More