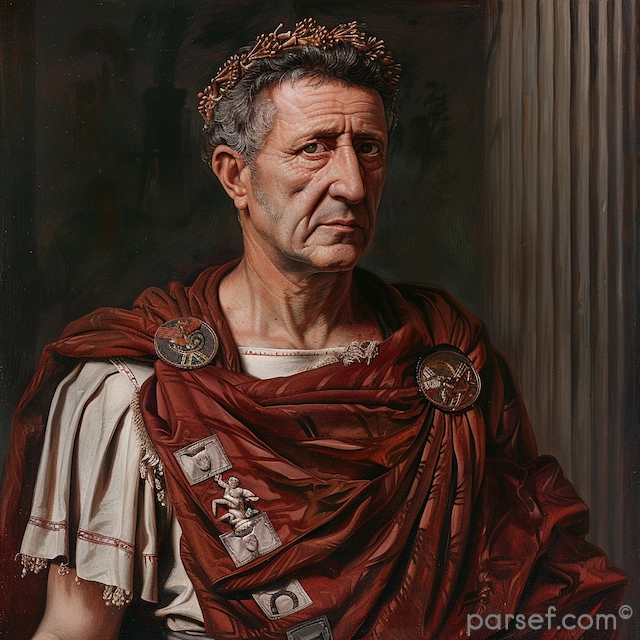
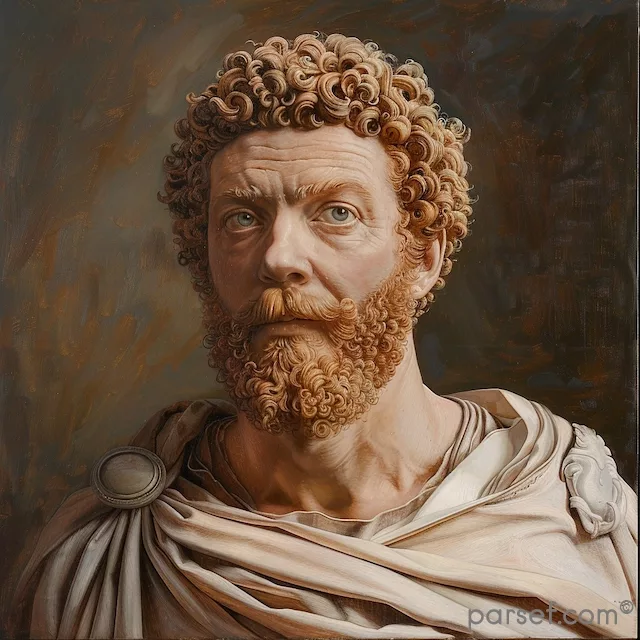
Didius Julianus: The Emperor Who Bought the Roman Empire

The year 193 AD was a tumultuous one for Rome. The assassination of the capable Pertinax plunged the empire into a crisis of leadership. The Praetorian Guard, the elite imperial bodyguards, found themselves without a master and, true to their corrupt nature, decided to auction off the imperial throne. In this extraordinary act, the once-mighty Roman Empire was reduced to a mere commodity.
The highest bidder in this shameful transaction was Marcus Didius Severus Julianus, a wealthy and influential senator. His path to power was as unconventional as it was scandalous. Julianus was a man of considerable wealth, but he lacked the military experience or political acumen that would typically be associated with an emperor. Yet, with a purse overflowing with gold, he was able to outbid his rivals for the coveted position.
The Praetorian Guard, ever focused on their own interests, readily accepted Julianus’ bid. The Senate, shocked and appalled by this blatant disregard for tradition and merit, was powerless to intervene. The once-proud institution had become a mere rubber stamp for the whims of a corrupt military force.
Julianus’ reign was as brief as it was disastrous. His legitimacy was questionable from the outset. He was seen as a puppet of the Praetorian Guard, a mere usurper of the imperial throne. The provinces, accustomed to strong, military leaders, were outraged by the selection of a civilian bureaucrat.
Moreover, Julianus proved to be utterly incapable of governing the vast Roman Empire. Lacking the necessary skills and authority, he was unable to quell the growing unrest within the empire. Meanwhile, ambitious generals in the provinces, such as Septimius Severus in Pannonia, saw an opportunity to seize power.
The final blow to Julianus’ short-lived reign came when Septimius Severus marched on Rome with his legions. The Praetorian Guard, realizing the futility of their support for the unpopular emperor, abandoned Julianus. The Senate, eager to distance itself from the disgraced ruler, condemned him to death.
In the end, Didius Julianus’ reign is a stark reminder of the decline of Roman values. The once-noble office of emperor had been reduced to a mere auction prize, a symbol of the empire’s moral and political decay. His brief tenure serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of placing power in the wrong hands.
The reign of Didius Julianus marked a turning point in Roman history. It ushered in a period of civil war and instability, known as the Year of the Five Emperors. Out of this chaos, Septimius Severus would eventually emerge victorious, ushering in a new dynasty and a period of relative stability.
Related Posts
Augustus: The Architect of Imperial Rome’s Golden Age
In the grand tapestry of ancient Rome's history, one name stands out as a pivotal figure who played a transformative role in shaping the destiny of an empire. That name is Augustus, the first Roman Emperor, whose reign marked the beginning of a remarkable era known as the Pax Romana...
Read MoreDriving Toward the Future: Innovations in Sustainable Automotive Technology
As the global focus sharpens on climate change, energy efficiency, and sustainable living, the automotive industry stands at a critical crossroads. Manufacturers, engineers, and policymakers are working in concert to reduce carbon emissions, enhance fuel economy, and reshape transportation for a cleaner tomorrow. At the heart of this revolution lies...
Read MoreRoman Emperors and the Importance of the Catholic Jubilee of 2025
Throughout history, Roman emperors have played a crucial role in shaping the world, particularly in their influence over politics, religion, and culture. Their legacy continues to resonate today, especially in the traditions of the Catholic Church. One such tradition is the Catholic Jubilee, a sacred year of forgiveness, renewal, and...
Read MoreYear of the Four Emperors: A Visual Timeline
📅 68 AD April: Galba, governor of Hispania Tarraconensis, and Vindex, governor of Gallia Lugdunensis, rebel against Emperor Nero.May: The Rhine legions defeat and kill Vindex in Gaul.June 8: The Senate declares Nero a public enemy.June 9: Nero commits suicide; Galba is recognized as emperor.November: Vitellius is appointed governor of Germania...
Read MoreThe Book of Revelation: A Historical and Theological Journey
The Book of Revelation, also known as the Apocalypse of John, is one of the most enigmatic and debated texts in the Christian biblical canon. Positioned as the final book of the New Testament, it has captivated theologians, historians, artists, and laypeople alike for nearly two millennia. Its vivid imagery,...
Read MoreNero: The Notorious Emperor Who Fiddled While Rome Burned
The name Nero is synonymous with tyranny, extravagance, and the infamous image of an emperor who, according to legend, played the fiddle while Rome was engulfed in flames. Nero's reign is a dark chapter in the history of the Roman Empire, marked by cruelty, decadence, and the disastrous Great Fire...
Read More