Sodom and Gomorrah: The Rise and Fall of Two Ancient Cities

Sodom and Gomorrah are two of the most infamous cities mentioned in ancient religious texts, notably the Bible. For centuries, they have symbolized divine judgment, moral depravity, and catastrophic destruction. Their story is told in the Book of Genesis, and echoes of their downfall reverberate through theology, archaeology, and mythology. But what do we truly know about these cities, and where exactly were they located?
Geographical and Biblical Context
According to the Hebrew Bible, Sodom and Gomorrah were located in the fertile plains of the Jordan River, near the Dead Sea, in a region called the Vale of Siddim. The cities were among five—Sodom, Gomorrah, Admah, Zeboiim, and Zoar—collectively known as the "cities of the plain."
You can explore the geographic positioning of these ancient cities using this detailed Sodom and Gomorrah map, which offers insights into the biblical topography and probable ancient trade routes.
Archaeologists and biblical scholars have long debated the precise location of these cities. Some believe the ruins may lie under the southern basin of the Dead Sea, possibly submerged by a cataclysmic geological event. Others speculate they could be located near modern-day Bab edh-Dhra and Numeira, sites that show signs of sudden and intense destruction.
The Narrative of Genesis
The story of Sodom and Gomorrah is most famously recounted in Genesis chapters 18 and 19. According to the text, God revealed to Abraham His intention to destroy the cities due to their grave sins, particularly their inhospitality, arrogance, and sexual immorality. Abraham famously pleaded on behalf of the cities, bargaining with God to spare them if even ten righteous individuals could be found. Ultimately, only Lot and his family were deemed righteous enough to be saved.
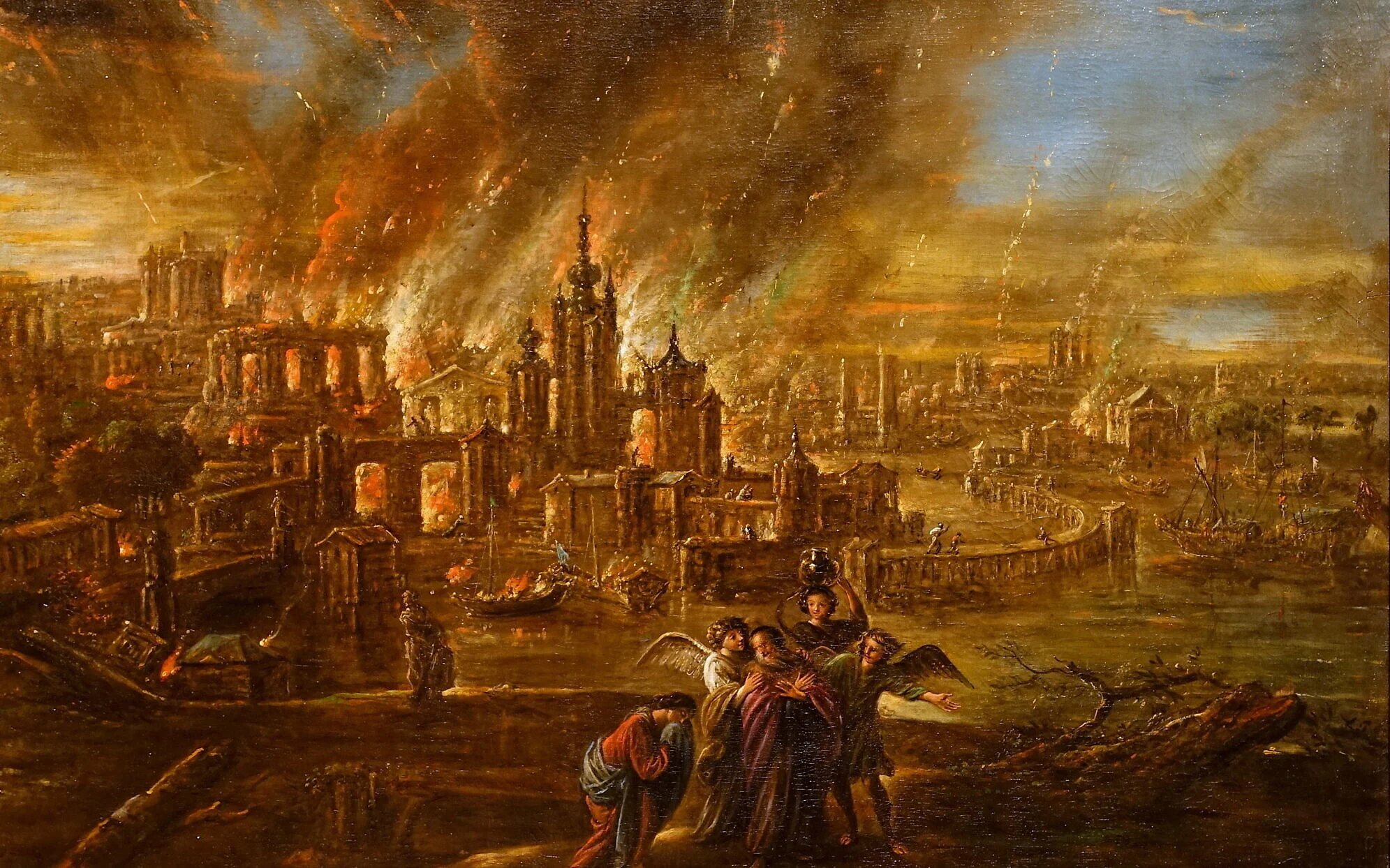
As fire and brimstone rained from the heavens, Sodom and Gomorrah were utterly annihilated. Lot and his family fled, instructed not to look back. Yet, Lot’s wife disobeyed and was turned into a pillar of salt. This dramatic story has left a powerful mark on Judeo-Christian teachings about sin, punishment, and divine justice.
Cultural and Religious Interpretations
Throughout the centuries, the tale of Sodom and Gomorrah has been interpreted in various ways. In Jewish tradition, the cities represented a failure of justice and hospitality. Christian teachings often emphasize the narrative as a warning against sexual immorality. In Islamic texts, the cities are similarly condemned, with Prophet Lut (Lot) serving as a moral guide in a corrupt society.
These interpretations are reflected across religious texts and have influenced moral and legal perspectives throughout history. The very word "sodomy" derives from the city's name, underscoring its association with transgressive behavior in Western moral discourse.
Archaeological Investigations
The mystery of Sodom and Gomorrah has attracted the attention of numerous archaeologists. The ruins at Bab edh-Dhra and Numeira, located southeast of the Dead Sea, are considered by some to be strong candidates for Sodom and Gomorrah, respectively. These sites were both destroyed in the Early Bronze Age, and evidence suggests sudden fiery destruction, consistent with the biblical account.
Interestingly, the region surrounding the southern Dead Sea is seismically active and contains high levels of natural asphalt and sulfur. A massive earthquake could have triggered the ignition of these volatile substances, creating a fiery explosion that could have inspired the biblical imagery of fire and brimstone.
For more information on the geographical layout of the ancient world in this region, see this Sodom and Egypt map and a Gomorrah map.
Scientific Theories and Natural Explanations
Beyond religious and archaeological interpretations, scientists have explored natural explanations for the cities' destruction. Some researchers have proposed a cosmic airburst, similar to the Tunguska event in 1908 Siberia, as the cause. A meteor explosion in the atmosphere could have incinerated the cities instantly, aligning with the account of a fiery destruction from above.
Others suggest that an earthquake may have ruptured natural gas pockets, causing explosions and fires. Given the region’s geology, such events were plausible and could explain the swift and total obliteration of once-thriving settlements.
Legacy and Cultural Impact
The legacy of Sodom and Gomorrah extends far beyond religious texts. They are referenced in literature, film, politics, and philosophy. They are invoked in discussions about morality, divine justice, and human behavior. Even modern science fiction and dystopian narratives have echoed the themes of Sodom’s fall—decay from within, warnings ignored, and ultimate ruin.
The question of their exact location still captures the imagination of explorers and scholars alike. Maps such as this Where Was Sodom and Gomorrah map and Sodom Gomorrah map continue to guide enthusiasts in their quest to uncover the lost cities.
Sodom and Gomorrah stand as potent symbols of ancient decadence and divine wrath. Whether viewed through the lens of scripture, archaeology, or science, their story continues to provoke debate, inspire awe, and warn future generations of the peril that accompanies moral decline and societal corruption.
Their legacy is preserved not just in sacred texts but in the very earth around the Dead Sea—a region that still whispers the legend of cities lost to flame and time.
Related Posts
From Scrolls to Stones: How Museums Document Biblical History
The Bible is more than just a collection of sacred texts—it’s a living document that has shaped centuries of religious, cultural, and historical movements. For thousands of years, it has been passed down through oral traditions, written manuscripts, and monumental inscriptions. The story of how these texts came to be,...
Read MoreAugustus: The Architect of Imperial Rome’s Golden Age
In the grand tapestry of ancient Rome's history, one name stands out as a pivotal figure who played a transformative role in shaping the destiny of an empire. That name is Augustus, the first Roman Emperor, whose reign marked the beginning of a remarkable era known as the Pax Romana...
Read MoreCaligula: Madness and Infamy in the Roman Empire
The name Caligula is synonymous with madness and infamy in the annals of Roman history. Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus Germanicus, known as Caligula, was the third Roman Emperor, and his tumultuous reign left an indelible mark of cruelty, debauchery, and tyranny. In this article, we delve into the life and...
Read MoreClaudius: The Unexpected Emperor and His Surprising Achievements
In the annals of Roman history, the name Claudius stands out as a remarkable story of an unexpected emperor who defied the odds and left behind a legacy of significant achievements. Often underestimated due to physical disabilities, Claudius rose to power and proved to be a capable and innovative ruler....
Read MoreRoman Festivals and Public Holidays
In ancient Rome, festivals and holidays were important days for the people to come together and perform religious rituals. Since the Roman calendar didn’t have weekends, these feriae (holidays) would provide days of rest from people’s regular routine. There were three kinds of Roman holidays: Conceptivae: These annual holidays had...
Read MoreThe Perfect French Riviera Wedding
The French Riviera: A Timeless Wedding Destination The French Riviera, or Côte d’Azur, is one of the world’s most iconic destinations for weddings, offering breathtaking coastlines, luxurious estates, and a romantic Mediterranean backdrop. But beyond its modern allure, this glamorous stretch of land has a deep-rooted history that dates back to...
Read More