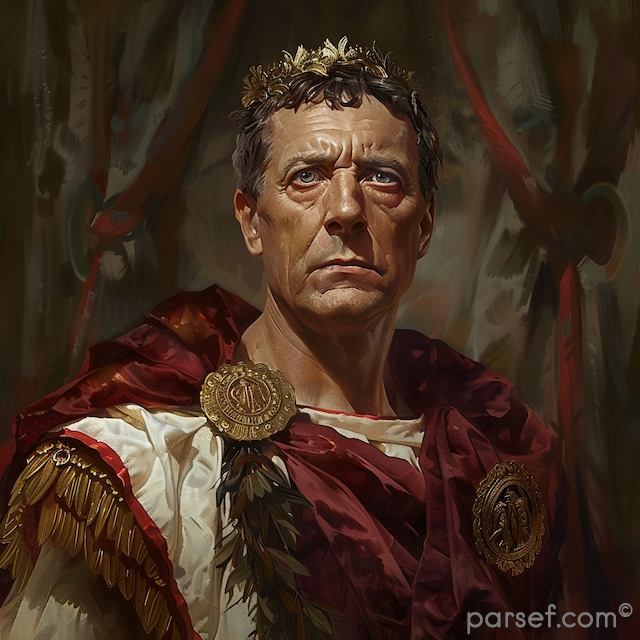
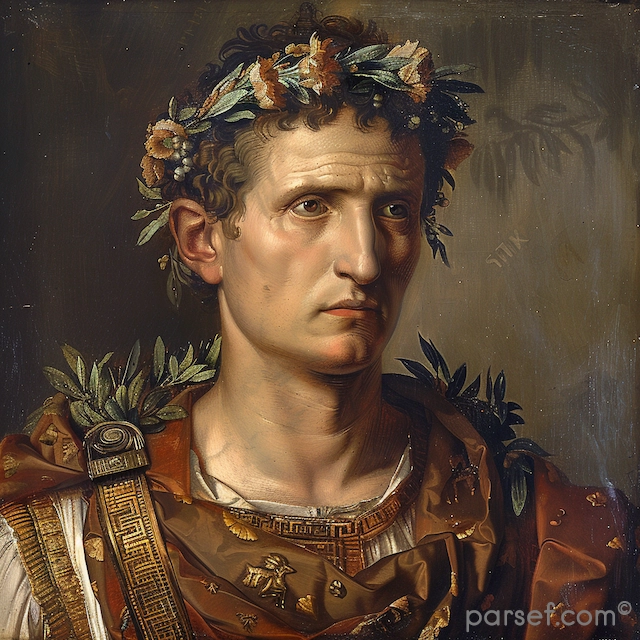
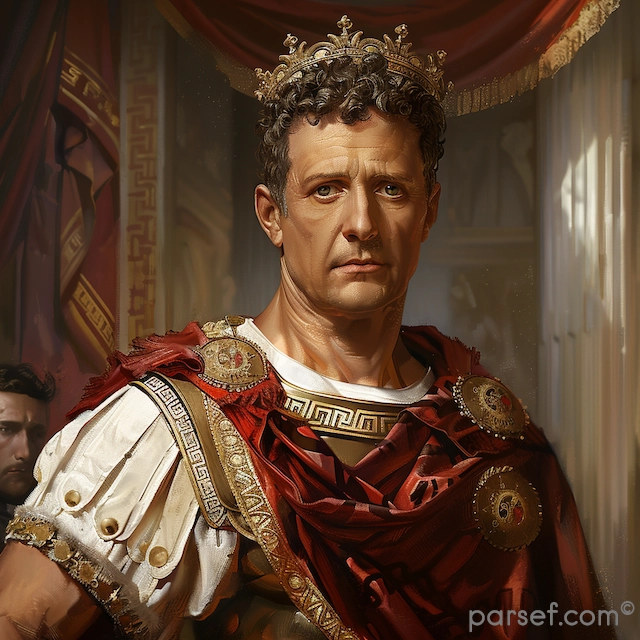
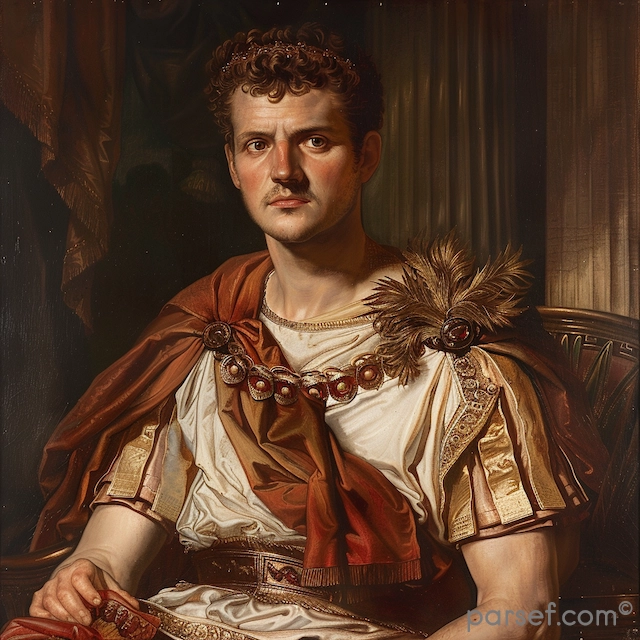
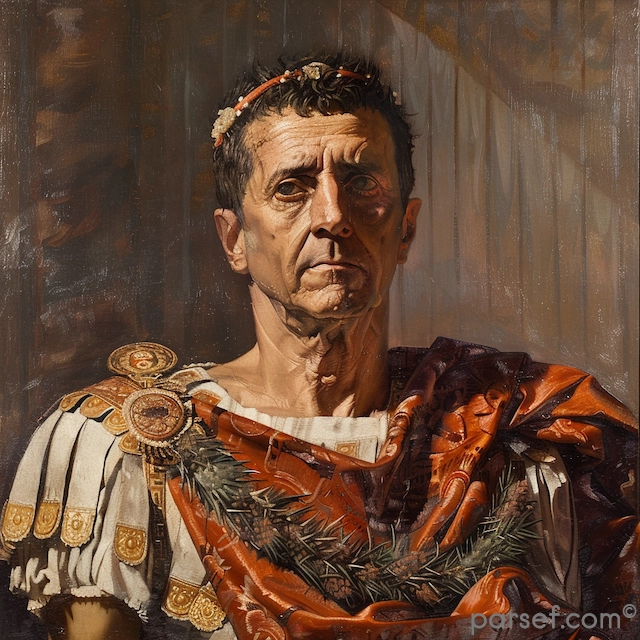
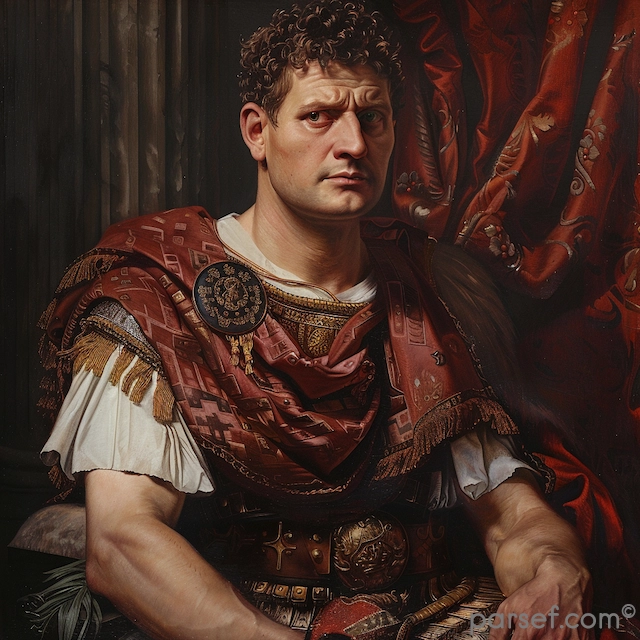
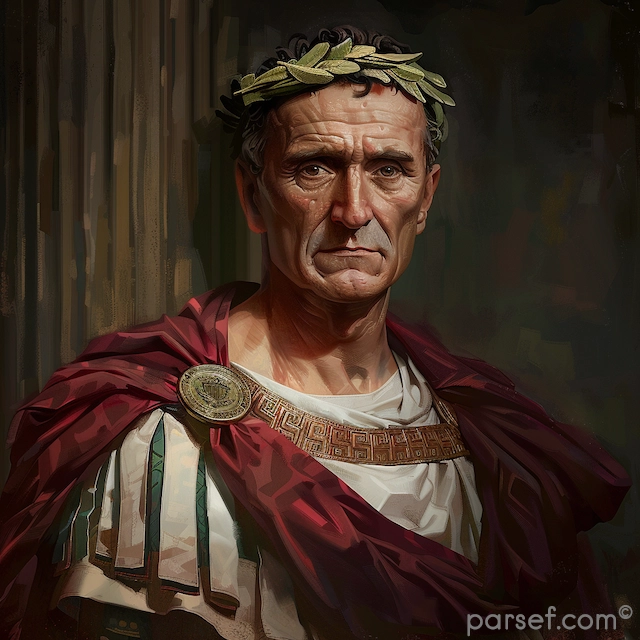
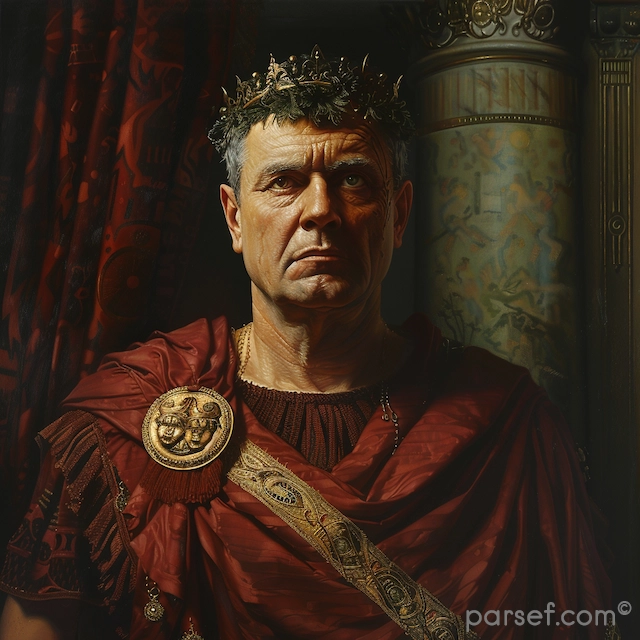
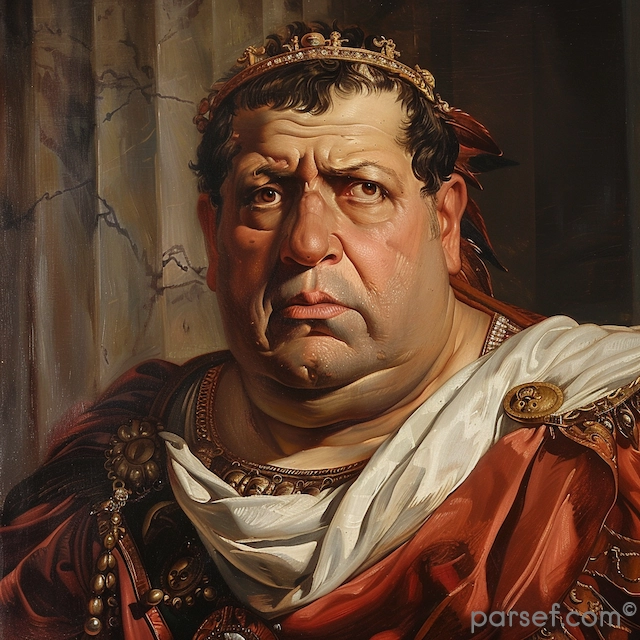
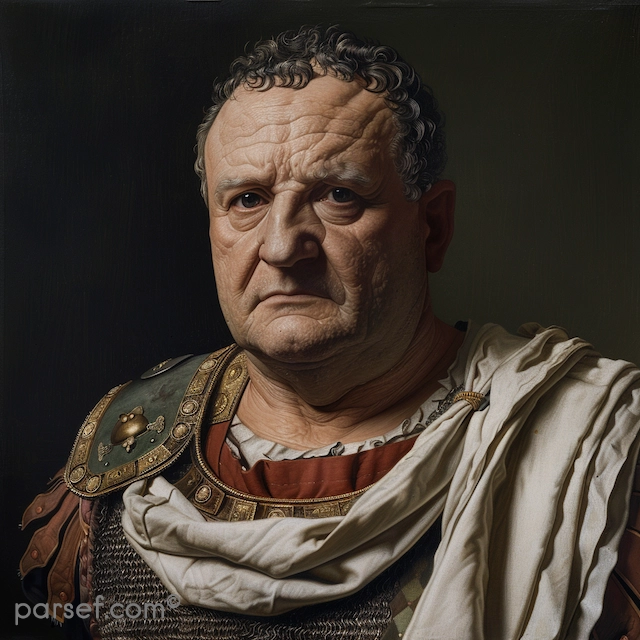
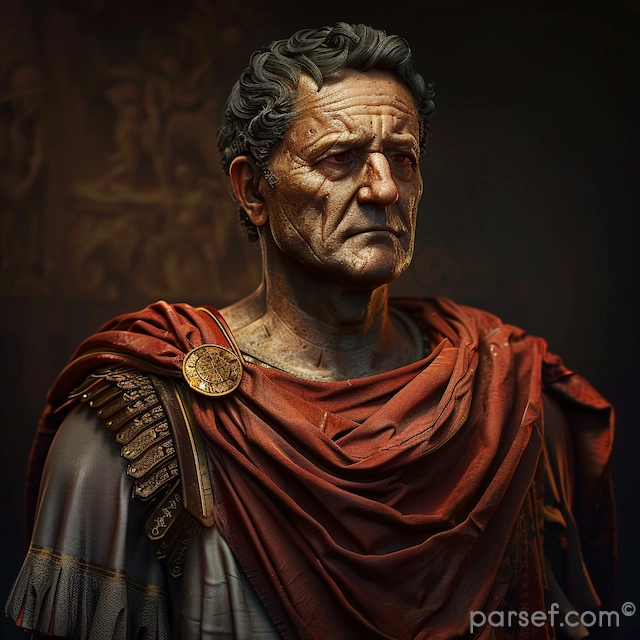
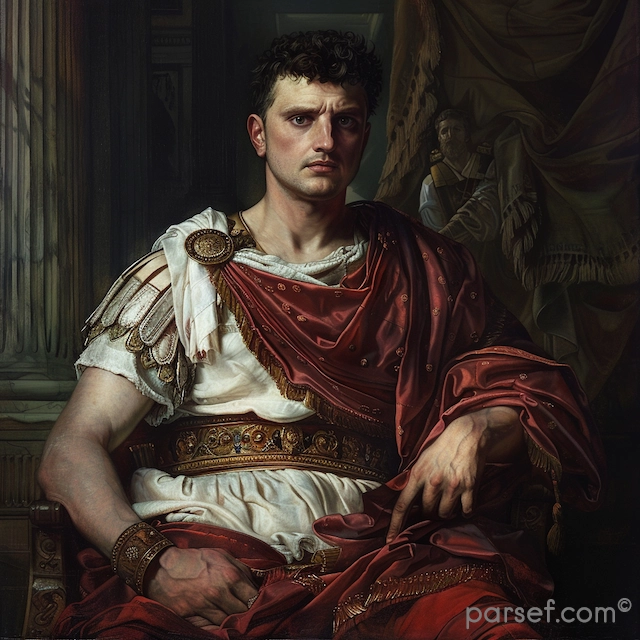
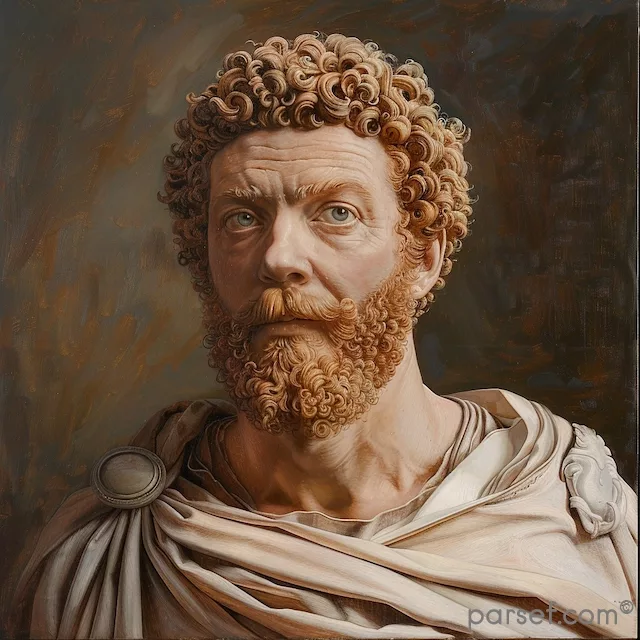
Nero: The Notorious Emperor Who Fiddled While Rome Burned
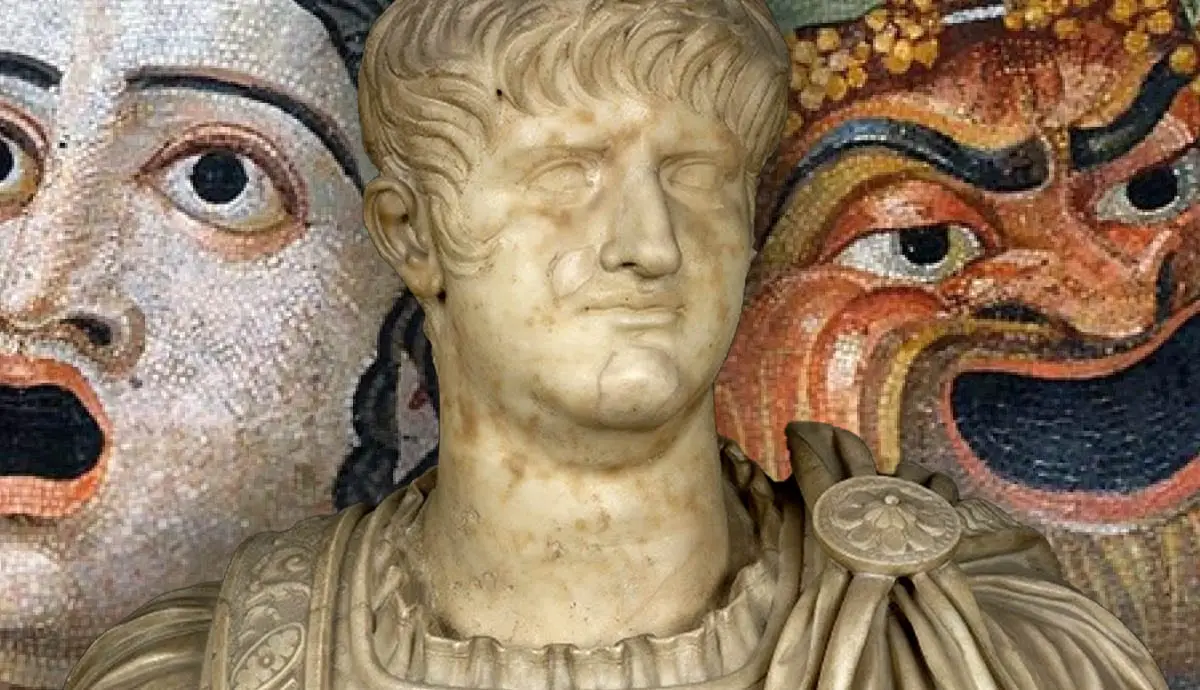

The name Nero is synonymous with tyranny, extravagance, and the infamous image of an emperor who, according to legend, played the fiddle while Rome was engulfed in flames. Nero's reign is a dark chapter in the history of the Roman Empire, marked by cruelty, decadence, and the disastrous Great Fire of Rome. In this article, we delve into the life and rule of Nero, shedding light on the controversial legacy of one of Rome's most notorious emperors.
Early Life and Ascension
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus, commonly known as Nero, was born in 37 CE. He became Emperor at the tender age of 16, succeeding his adopted father Claudius. Initially, Nero's reign was marked by optimism, as many hoped for a return to stability and order after the tumultuous rule of his predecessors.
A Reign of Excess and Cruelty
Unfortunately, Nero's rule took a dark turn. He became known for his extravagant lifestyle, indulging in lavish banquets, chariot races, and artistic pursuits. His excessive spending drained the Roman treasury, causing economic hardships for the empire.
Nero's cruelty became increasingly evident as he purged perceived threats to his power. The most infamous of these purges was the execution of his mother, Agrippina the Younger, and his alleged role in the poisoning of his stepbrother and wife.
The Great Fire of Rome
Nero's name is forever associated with the Great Fire of Rome in 64 CE. While it's unlikely that he actually fiddled during the fire, historical accounts suggest that he was indifferent to the disaster and may have even viewed it as an opportunity. The fire raged for days, destroying vast portions of the city and leaving thousands homeless.
In the aftermath, Nero faced widespread criticism for his response. He shifted blame onto Christians, leading to the first major persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire. Nero's actions during and after the fire further eroded his standing among the Roman population.
Downfall and Death
Nero's excesses, cruelty, and extravagance ultimately led to his downfall. In 68 CE, a rebellion led by prominent figures within the Roman government and military forced Nero to flee Rome. Facing imminent capture and execution, Nero took his own life in 68 CE, marking the end of his tumultuous reign.
Legacy of Infamy
Nero's legacy is one of infamy and notoriety. He is remembered for his despotism, mismanagement, and the devastation caused by the Great Fire of Rome. His reign marked a low point in Roman imperial history, and he remains a symbol of tyranny and excess.
Nero's reign stands as a stark reminder of the dangers of absolute power and unchecked ambition. His notoriety continues to captivate historians and storytellers alike, serving as a cautionary tale of the destructive potential of a leader who places personal gratification above the welfare of the empire and its people.
Related Posts
Severus Alexander: The Emperor Who Faced Down Crisis and Attempted to Restore Order
Severus Alexander, often overshadowed by the more flamboyant and controversial emperors who preceded him, was a ruler who ascended to the imperial throne at a time of profound crisis. His reign, while ultimately brief, was marked by a determined effort to restore order and stability to the Roman Empire. Grandson of...
Read MoreYear of the Four Emperors: A Visual Timeline
📅 68 AD April: Galba, governor of Hispania Tarraconensis, and Vindex, governor of Gallia Lugdunensis, rebel against Emperor Nero.May: The Rhine legions defeat and kill Vindex in Gaul.June 8: The Senate declares Nero a public enemy.June 9: Nero commits suicide; Galba is recognized as emperor.November: Vitellius is appointed governor of Germania...
Read MoreMacrinus: The First Equestrian Emperor and His Brief Attempt to Stabilize Rome
Opilius Macrinus, an unexpected figure in the annals of Roman history, ascended to the imperial throne in 217 AD after the assassination of Caracalla. Unlike his predecessors, who hailed from the senatorial aristocracy, Macrinus was an eques, a member of the equestrian order, a social class traditionally associated with business...
Read MoreSodom and Gomorrah: The Rise and Fall of Two Ancient Cities
Sodom and Gomorrah are two of the most infamous cities mentioned in ancient religious texts, notably the Bible. For centuries, they have symbolized divine judgment, moral depravity, and catastrophic destruction. Their story is told in the Book of Genesis, and echoes of their downfall reverberate through theology, archaeology, and mythology....
Read MoreBonsai Trees: The Art, Care, and Beauty of Miniature Trees
Bonsai trees are more than just plants—they are living works of art, shaped and nurtured over time to reflect nature’s beauty in miniature form. Originating from ancient Asian traditions, bonsai trees symbolize harmony, patience, and balance, making them a meaningful and meditative hobby for plant lovers worldwide. Whether you're a...
Read MoreJerusalem Artisan Rosaries Handcrafted vs. Mass-Produced
In a world full of fast-made products, many believers are looking for devotional items that feel faithful, lasting, and true. Jerusalem Artisan Rosaries Handcrafted vs. Mass-Produced is more than a comparison—it’s a prayerful question: “What will help me (or someone I love) stay close to Jesus day after day?” This...
Read More