Trajan: Expanding the Roman Empire to Its Zenith
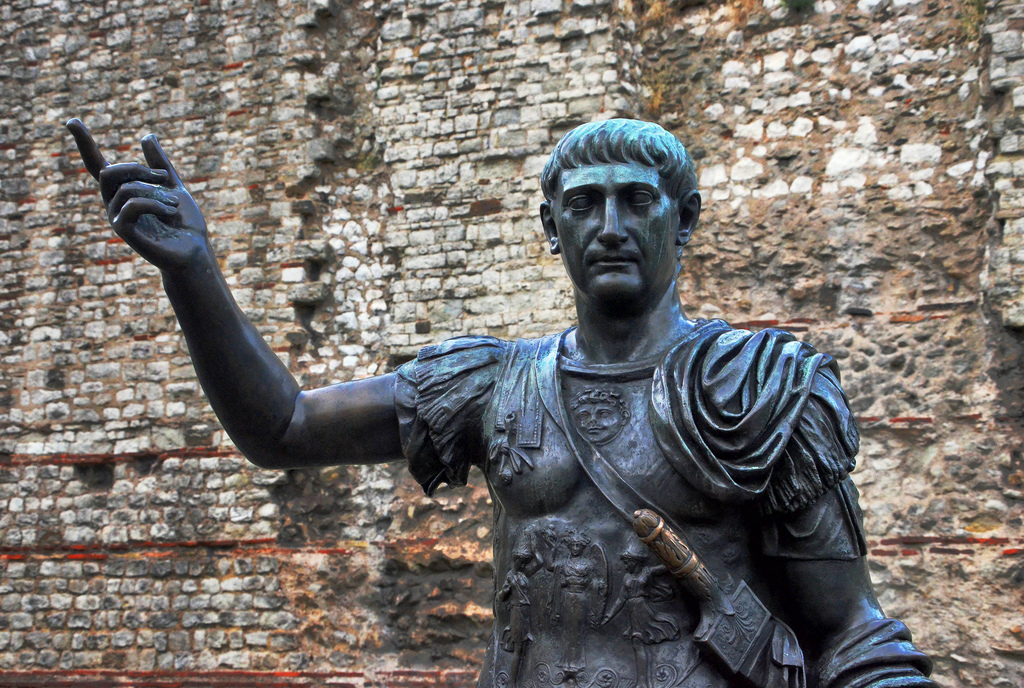

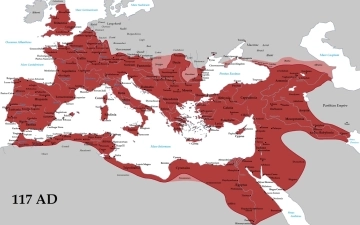
The Roman Empire, at its zenith, was a sprawling realm that stretched from Britannia in the north to Egypt in the south, and from Hispania in the west to Mesopotamia in the east. Among the emperors who played a pivotal role in this expansion and solidified Rome's dominance was Trajan. His reign, from 98 to 117 CE, marked a high point in Roman history, both in terms of territorial conquest and cultural achievement. In this article, we delve into the life and accomplishments of Trajan, the emperor who expanded the Roman Empire to its zenith.
Early Life and Rise to Power
Trajan, born Marcus Ulpius Trajanus in 53 CE, came from a distinguished provincial family in Spain. His family had a history of military service, and Trajan's own career followed suit. He rose through the ranks of the Roman military, earning a reputation for competence and leadership.
Adoption and Accession
Trajan's path to the imperial throne was unconventional. He was not born into the Julio-Claudian dynasty but was adopted by Emperor Nerva, who saw in Trajan a capable and deserving successor. This adoption established a tradition of adopting capable successors, known as the "Adoptive Emperors."
Conquests and Expansion
Trajan's reign is most renowned for its extensive military campaigns. He launched several successful campaigns that significantly expanded the Roman Empire:
- Dacia (Modern-Day Romania): Trajan's conquest of Dacia, a prosperous region north of the Danube, brought vast wealth and resources to Rome.
- Parthia (Modern-Day Iran): His eastern campaigns led to the capture of the Parthian capital, Ctesiphon, and briefly brought Mesopotamia under Roman control.
- Armenia and Mesopotamia: Trajan's conquests in these regions further extended the Roman frontiers in the east.
These campaigns contributed to the territorial peak of the Roman Empire, which stretched from the Atlantic Ocean to the Persian Gulf.
Architectural and Cultural Achievements
Trajan was not only a skilled military strategist but also a patron of the arts and architecture. He commissioned several impressive public works, including Trajan's Column in Rome, which commemorates his Dacian campaigns and serves as a historical record of the era. He also undertook extensive public building projects, including roads, bridges, and aqueducts, enhancing the infrastructure of the empire.
Death and Legacy
Trajan's reign came to an end with his death in 117 CE. He was succeeded by his adopted son, Hadrian. Trajan's legacy endures as one of the "Five Good Emperors" of Rome, a period characterized by stability, prosperity, and competent governance.
Trajan's military conquests and cultural contributions left an indelible mark on Roman history. His reign is often regarded as the pinnacle of Roman expansion and power, and his legacy as a wise and capable ruler continues to be celebrated in both historical records and modern scholarship.
Trajan's reign represents a golden era of Roman history marked by territorial expansion, cultural achievements, and effective governance. His ability to combine military prowess with a commitment to civic and cultural development solidified his place among Rome's greatest emperors.
Related Posts
Macrinus: The First Equestrian Emperor and His Brief Attempt to Stabilize Rome
Opilius Macrinus, an unexpected figure in the annals of Roman history, ascended to the imperial throne in 217 AD after the assassination of Caracalla. Unlike his predecessors, who hailed from the senatorial aristocracy, Macrinus was an eques, a member of the equestrian order, a social class traditionally associated with business...
Read MoreCaracalla: The Emperor of Bloodshed and the Architect of Roman Citizenship
Caracalla, son of the formidable Emperor Septimius Severus, is a complex and contradictory figure in Roman history. Often remembered for his brutality and paranoia, he is equally renowned for one of the most far-reaching edicts in Roman law. His reign was marked by a tumultuous blend of violence and reform. Shortly...
Read MoreA Journey Through Time: Mapping Ancient Rome and Jerusalem
For centuries, Rome and Jerusalem have captivated historians and travelers alike. These two powerful cities, though geographically distant, were intertwined throughout much of their ancient history. But how close were they? Let's explore maps depicting these ancient cities and their respective empires. The Mediterranean World: A Roman Sea During the height of...
Read MoreAugustus: The Architect of Imperial Rome’s Golden Age
In the grand tapestry of ancient Rome's history, one name stands out as a pivotal figure who played a transformative role in shaping the destiny of an empire. That name is Augustus, the first Roman Emperor, whose reign marked the beginning of a remarkable era known as the Pax Romana...
Read MoreThe Book of Revelation: A Historical and Theological Journey
The Book of Revelation, also known as the Apocalypse of John, is one of the most enigmatic and debated texts in the Christian biblical canon. Positioned as the final book of the New Testament, it has captivated theologians, historians, artists, and laypeople alike for nearly two millennia. Its vivid imagery,...
Read MoreNero: The Notorious Emperor Who Fiddled While Rome Burned
The name Nero is synonymous with tyranny, extravagance, and the infamous image of an emperor who, according to legend, played the fiddle while Rome was engulfed in flames. Nero's reign is a dark chapter in the history of the Roman Empire, marked by cruelty, decadence, and the disastrous Great Fire...
Read More