Ramoth-Gilead: The Ancient Stronghold of Israel
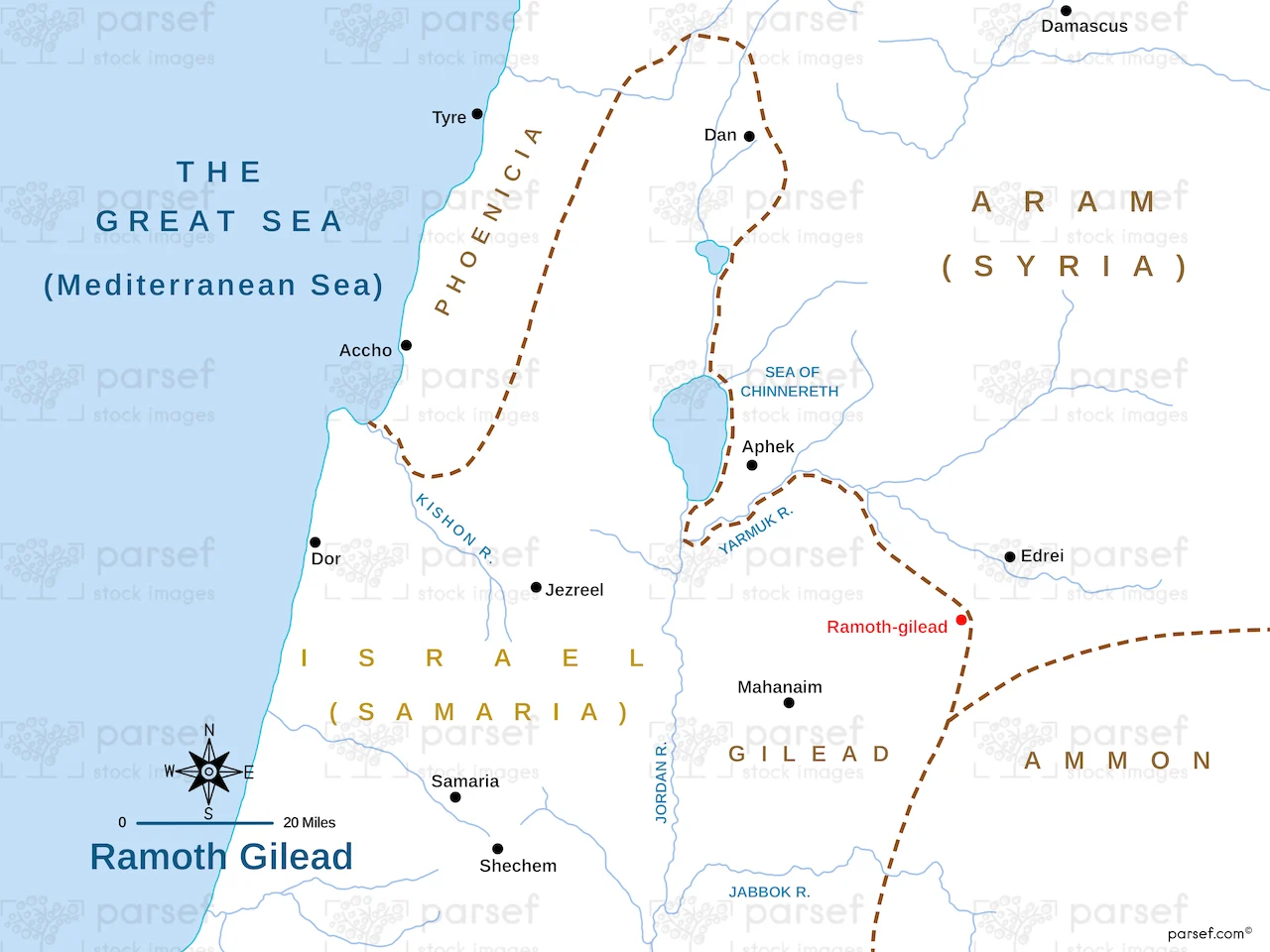
Ramoth-Gilead, an ancient city of great biblical and historical significance, was a major stronghold located in the region of Gilead, east of the Jordan River. The city, often mentioned in the Old Testament, played a crucial role in the territorial struggles between Israel and its neighboring nations. Today, the exact location of Ramoth-Gilead remains debated, but most scholars associate it with modern Tell er-Rumeith or a nearby site in present-day Jordan. If one looks at a Ramoth-Gilead map, it would place the city strategically in the mountainous region of Gilead, providing a vantage point for military and trade purposes.
Ramoth-Gilead in the Bible
Ramoth-Gilead appears several times in the Old Testament, particularly in the books of Deuteronomy, Joshua, 1 Kings, and 2 Chronicles. It was one of the cities designated as a City of Refuge (Joshua 20:8), where those who had accidentally committed manslaughter could flee for protection until a fair trial was conducted.
The city was also a Levitical city (Joshua 21:38), assigned to the tribe of Gad and given to the Levites, who were responsible for religious duties and temple service. Being one of the six cities of refuge, it had a special status within Israelite society.
The Battles for Ramoth-Gilead
Due to its strategic location, Ramoth-Gilead became a contested site between Israel and Aram (modern Syria). Several key battles were fought over control of this fortress.
1. The Battle of King Ahab (1 Kings 22)
One of the most famous events associated with Ramoth-Gilead is the battle involving King Ahab of Israel. In 1 Kings 22, Ahab, in alliance with Jehoshaphat, king of Judah, sought to reclaim Ramoth-Gilead from the Arameans. The prophet Micaiah warned Ahab against going to battle, predicting his demise. However, Ahab ignored the prophecy and disguised himself to avoid being targeted. Despite his efforts, he was struck by an arrow and later died, fulfilling Micaiah’s prophecy.
2. Jehu’s Revolt and the Death of Joram (2 Kings 9)
Ramoth-Gilead also played a pivotal role in the downfall of the Omride dynasty. In 2 Kings 9, Joram (Jehoram), king of Israel, was wounded in battle while defending Ramoth-Gilead against the Arameans. During this time, the prophet Elisha sent a young prophet to anoint Jehu as king of Israel at Ramoth-Gilead, setting off a revolution. Jehu then traveled to Jezreel, where he assassinated Joram, bringing an end to the dynasty of Ahab.
Historical and Archaeological Evidence
While no definitive archaeological evidence confirms the precise location of Ramoth-Gilead, scholars suggest it was situated in northern Gilead, likely near modern Tell er-Rumeith or Umm Qais (Gadara). Excavations in these areas have uncovered remnants of ancient fortifications, pottery, and inscriptions that suggest a history of warfare and settlement in the region.
The Mesha Stele, an ancient Moabite inscription dating to the 9th century BCE, mentions conflicts between Moab and Israel in Gilead, further confirming the region’s importance in biblical times.
Ramoth-Gilead’s Role in Trade and Military Strategy
Beyond its military significance, Ramoth-Gilead was a key trade hub along ancient caravan routes connecting Israel, Aram (Syria), and Mesopotamia. Its high elevation allowed it to serve as a fortified outpost, protecting the eastern frontier of Israel from invasions. Control over Ramoth-Gilead meant dominance over valuable trade routes and access to vital resources.
Ramoth-Gilead remains one of the most historically and biblically significant cities of ancient Israel. From its designation as a City of Refuge to its role in the political and military conflicts of Israel and Aram, it has been a focal point of biblical narratives and historical battles. While its exact location is still debated, its impact on the history of the ancient Near East is undeniable.
Related Posts
A Journey Through Time: Mapping Ancient Rome and Jerusalem
For centuries, Rome and Jerusalem have captivated historians and travelers alike. These two powerful cities, though geographically distant, were intertwined throughout much of their ancient history. But how close were they? Let's explore maps depicting these ancient cities and their respective empires. The Mediterranean World: A Roman Sea During the height of...
Read MoreThe Book of Revelation: A Historical and Theological Journey
The Book of Revelation, also known as the Apocalypse of John, is one of the most enigmatic and debated texts in the Christian biblical canon. Positioned as the final book of the New Testament, it has captivated theologians, historians, artists, and laypeople alike for nearly two millennia. Its vivid imagery,...
Read MoreBonsai Trees: The Art, Care, and Beauty of Miniature Trees
Bonsai trees are more than just plants—they are living works of art, shaped and nurtured over time to reflect nature’s beauty in miniature form. Originating from ancient Asian traditions, bonsai trees symbolize harmony, patience, and balance, making them a meaningful and meditative hobby for plant lovers worldwide. Whether you're a...
Read MoreFrom Scrolls to Stones: How Museums Document Biblical History
The Bible is more than just a collection of sacred texts—it’s a living document that has shaped centuries of religious, cultural, and historical movements. For thousands of years, it has been passed down through oral traditions, written manuscripts, and monumental inscriptions. The story of how these texts came to be,...
Read MoreHerod’s Temple: A Marvel of Ancient Architecture and Its Biblical Significance
Herod’s Temple, also known as the Second Temple or the Herodian Temple, holds a central place in biblical history and Jewish heritage. Built by King Herod the Great during the 1st century BCE, this architectural masterpiece served as the spiritual heart of Judaism and a pivotal location in the narratives...
Read MoreGeta: The Tragic Co-Emperor Whose Life Was Cut Short by Fraternal Rivalry
Geta, the younger son of Septimius Severus, is a figure largely overshadowed by his more domineering brother, Caracalla. Often relegated to the role of the quiet, less ambitious sibling, Geta’s life was tragically cut short by a family feud that shook the Roman Empire to its core. Unlike his brother, Geta...
Read More