The Book of Revelation: A Historical and Theological Journey

The Book of Revelation, also known as the Apocalypse of John, is one of the most enigmatic and debated texts in the Christian biblical canon. Positioned as the final book of the New Testament, it has captivated theologians, historians, artists, and laypeople alike for nearly two millennia. Its vivid imagery, symbolic language, and prophetic tone have inspired countless interpretations, ranging from the strictly literal to the allegorical and mystical.
Authorship and Historical Context
Traditionally, the book is attributed to John the Apostle, the beloved disciple of Jesus. However, scholarly consensus is more nuanced. The text itself only identifies the author as "John," and there is considerable debate as to whether this John is the Apostle, a different early Christian prophet, or even a pseudonymous figure. Most scholars date the writing of Revelation to around 95-96 CE during the reign of the Roman Emperor Domitian.
This period was marked by increasing tension and persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire. The early Christian community faced threats both from outside, in the form of Roman imperial cult worship, and from within, through doctrinal disagreements. Revelation is believed to be a response to these crises—a work of encouragement and admonition that uses apocalyptic imagery to affirm God's ultimate sovereignty and justice.
Structure and Symbolism
The Book of Revelation is structured in a series of visions experienced by the author while exiled on the island of Patmos. It begins with letters to seven churches in Asia Minor, offering praise and critique. From there, the text unfolds in a series of symbolic visions involving scrolls, seals, trumpets, bowls, beasts, and a cosmic battle between good and evil.
A central theme is the unveiling (or "apocalypse") of divine truth and the eventual triumph of Christ over the forces of evil. The imagery draws heavily from Old Testament texts such as Daniel, Ezekiel, and Isaiah, weaving a rich tapestry of theological and eschatological meaning. The number seven, signifying completeness, appears frequently—seven churches, seven seals, seven trumpets, seven bowls—underscoring the divine orchestration of history.
To help understand the chronological flow and symbolic elements, many readers consult a revelation timeline, which visually outlines the complex series of events described in the text. Such resources are invaluable for interpreting the densely layered narrative and for connecting various events across different visions.
Interpretative Approaches
Over the centuries, Christians have approached Revelation from multiple perspectives:
- Preterist View: Sees most of Revelation's events as already fulfilled in the first century, often related to the fall of Jerusalem and the persecution under Rome.
- Historicist View: Interprets Revelation as a broad survey of church history from the time of Christ to the present.
- Futurist View: Considers most of the book to be prophetic, awaiting future fulfillment.
- Idealist (or Symbolic) View: Understands Revelation as a timeless allegory of the struggle between good and evil, not tied to specific historical events.
These interpretative frameworks are often blended, and debates continue regarding their merits. A timeline of Revelation can be particularly helpful for those exploring the futurist perspective, which seeks to align the visions with anticipated end-times events.
Major Themes and Theological Implications
- Judgment and Justice: A recurring message is that divine judgment will fall upon the wicked—whether represented by the Beast, Babylon, or the dragon.
- Perseverance and Faithfulness: The early Christians are exhorted to remain steadfast in the face of suffering.
- Hope and Restoration: The climax of Revelation is not destruction but renewal—the New Heaven and New Earth, where God dwells with humanity.
- Worship and Sovereignty: Scenes of heavenly worship remind readers of God's supreme power and glory.
Understanding the sequence of events and the broader theological arc is made clearer with resources like a book of Revelation timeline, which break down the book's visions into digestible segments.
Artistic and Cultural Impact
The Book of Revelation has deeply influenced Christian liturgy, art, literature, and music. Medieval artists rendered its visions in vivid frescoes; composers like Handel echoed its themes in oratorios; modern films and novels borrow liberally from its motifs. The idea of an "apocalypse" has transcended theology to become a cultural archetype for cataclysm and rebirth.
This widespread influence underscores the importance of understanding the timeline of the Book of Revelation in both religious and secular contexts.
The Book of Revelation continues to inspire awe and provoke debate. It is a text that resists easy interpretation but rewards diligent study. Whether one views it as a prophecy, a pastoral letter, a political critique, or a mystical vision, Revelation offers a compelling vision of cosmic justice and divine triumph. For those seeking to navigate its intricacies, consulting a timeline of events in the Book of Revelation provides a valuable framework for deeper understanding.
In exploring the Book of Revelation timeline of events, readers gain not only insight into the apocalyptic imagination of early Christianity but also a renewed appreciation for the enduring power of this remarkable text.
Related Posts
Creating a Welcoming Worship Space: Tips for Choosing Inclusive Church Chairs
An inviting and inclusive church environment is paramount for fostering a strong sense of community and belonging. While theological beliefs and welcoming greetings are essential, the physical space itself also plays a significant role. One often-overlooked element that can significantly impact inclusivity is your church seating. This post dives...
Read MoreFrom Scrolls to Stones: How Museums Document Biblical History
The Bible is more than just a collection of sacred texts—it’s a living document that has shaped centuries of religious, cultural, and historical movements. For thousands of years, it has been passed down through oral traditions, written manuscripts, and monumental inscriptions. The story of how these texts came to be,...
Read MoreHow Online Tutoring Builds Stronger Foundations in Chemistry
Understanding chemistry often feels like learning a new language—symbols, equations, and reactions that demand more than just memorization. This is where online tutoring steps in as a game-changer. By offering personalized attention, real-time feedback, and flexible pacing, online tutoring helps students grasp core principles with confidence. It transforms abstract chemical...
Read MoreA Journey Through Time: Mapping Ancient Rome and Jerusalem
For centuries, Rome and Jerusalem have captivated historians and travelers alike. These two powerful cities, though geographically distant, were intertwined throughout much of their ancient history. But how close were they? Let's explore maps depicting these ancient cities and their respective empires. The Mediterranean World: A Roman Sea During the height of...
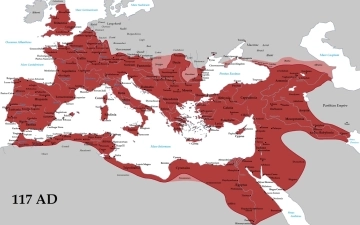
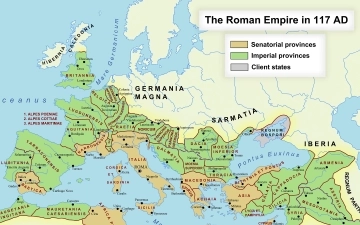
Read MoreThe Colossal Footprint: Exploring the Roman Empire at its Greatest Extent
The Roman Empire, a name that evokes images of gladiatorial combat, sprawling aqueducts, and stoic emperors, wasn't just a powerful state; it was a colossal empire that stretched across continents. But how vast was its reach at its zenith? This post delves into the greatest extent of the Roman Empire,...
Read MoreNero: The Notorious Emperor Who Fiddled While Rome Burned
The name Nero is synonymous with tyranny, extravagance, and the infamous image of an emperor who, according to legend, played the fiddle while Rome was engulfed in flames. Nero's reign is a dark chapter in the history of the Roman Empire, marked by cruelty, decadence, and the disastrous Great Fire...
Read More