Elagabalus: The Controversial Reign of Rome’s Youngest Emperor and His Religious Revolution

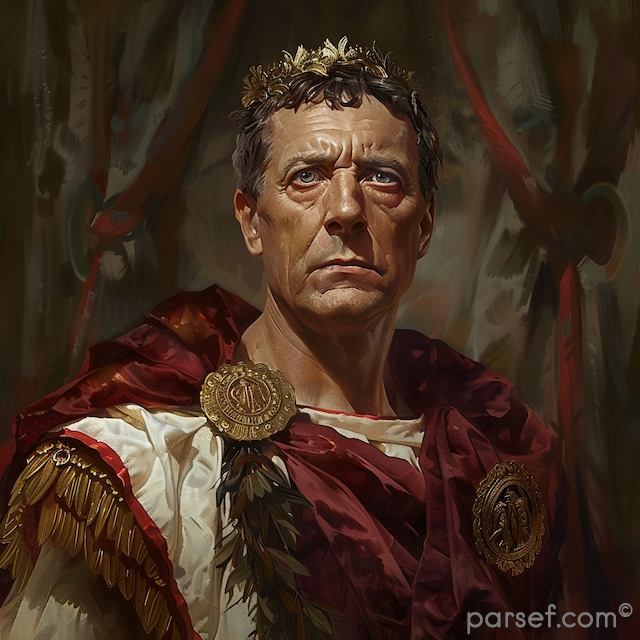
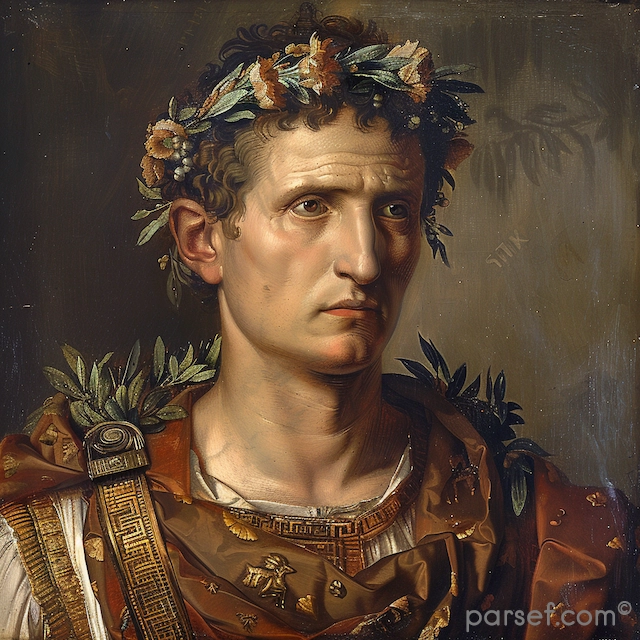
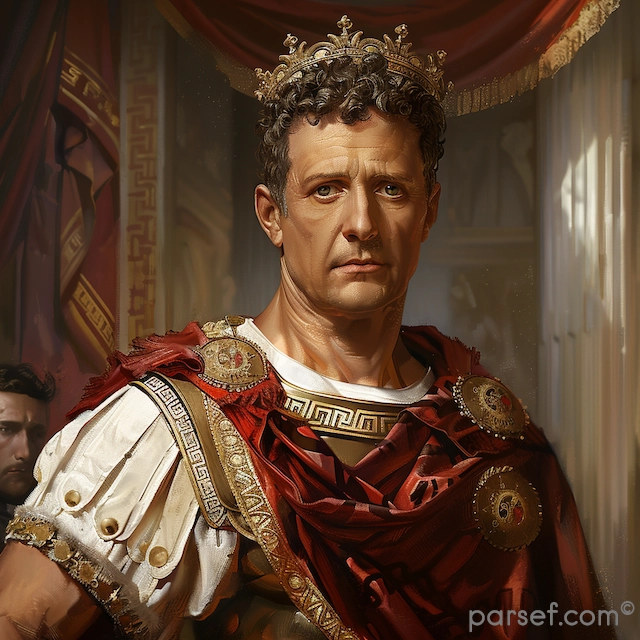
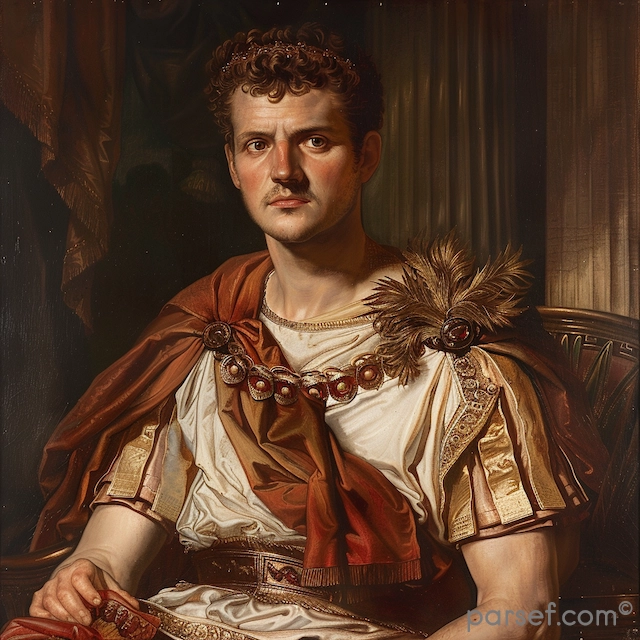
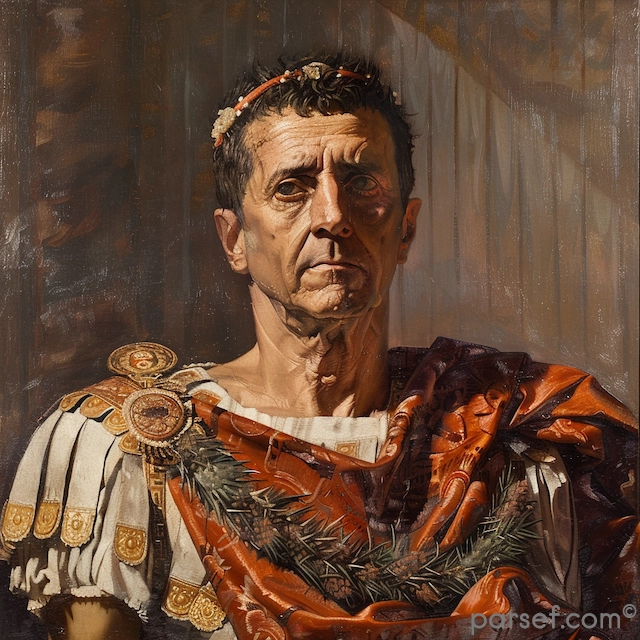
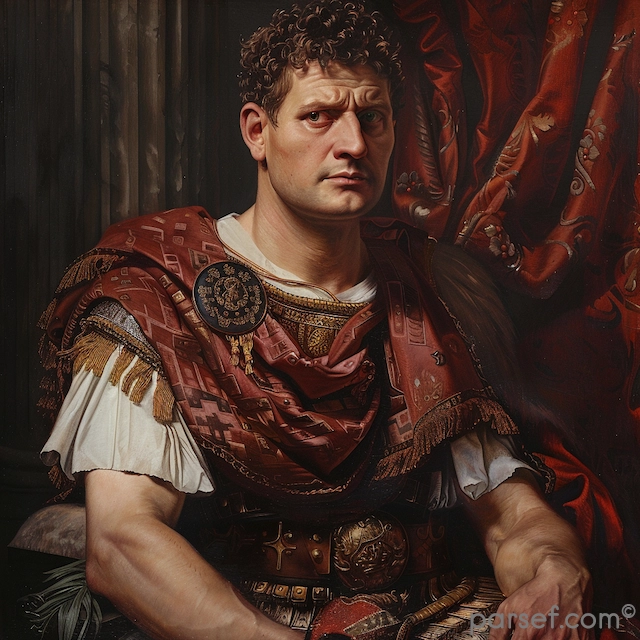
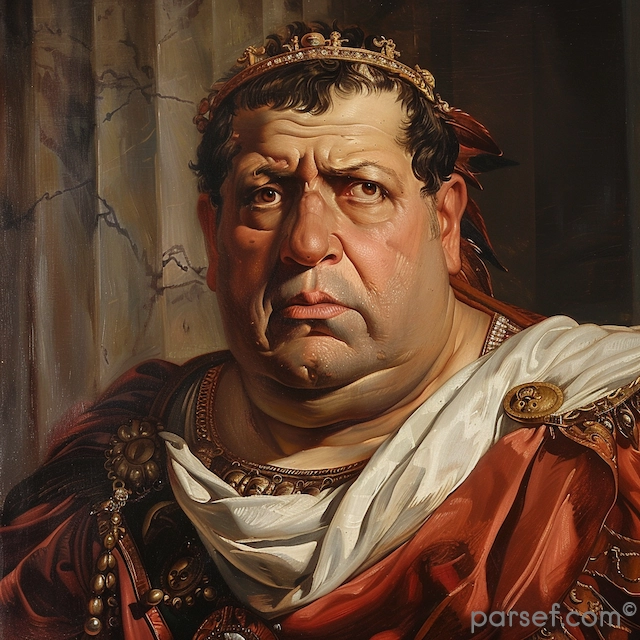
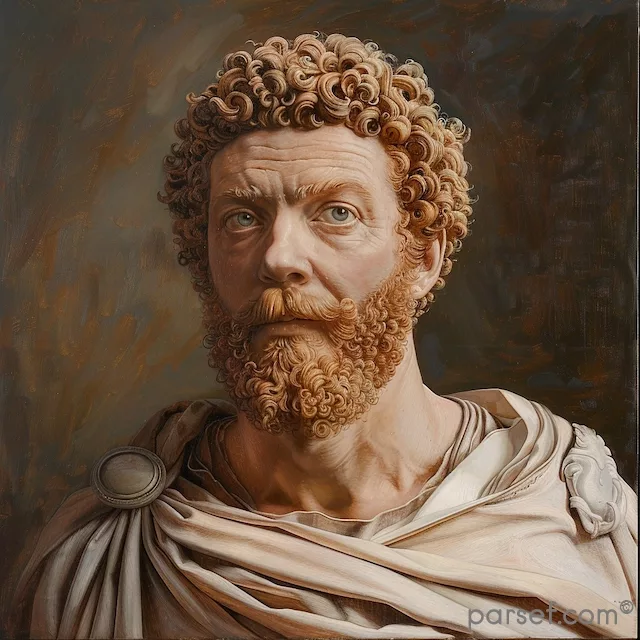
Elagabalus, born Varius Avitus Bassianus, is one of the most enigmatic and controversial figures in Roman history. Elevated to the imperial throne at the tender age of fourteen, his reign was marked by extravagance, scandal, and a radical religious transformation.
His rise to power was as dramatic as his subsequent reign. A distant cousin of Caracalla, Elagabalus was proclaimed emperor by the Praetorian Guard following the assassination of Macrinus. His mother, Julia Soaemias, and grandmother, Julia Maesa, were instrumental in securing his position.
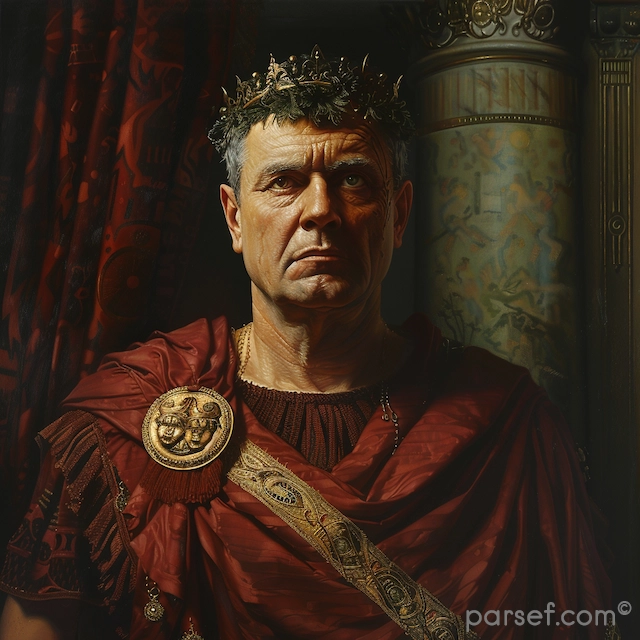
Elagabalus' reign is synonymous with religious innovation, or perhaps more accurately, revolution. A devout worshipper of the Syrian sun god Elagabal, he introduced the cult to Rome, replacing traditional Roman deities with his own. The emperor constructed a lavish temple to the god on the Palatine Hill, the heart of the Roman world. The centerpiece of this temple was a large black stone, believed to be a meteorite, which was said to be the physical manifestation of the deity.
Elagabalus' religious zeal extended beyond mere worship. He insisted that Roman senators and high-ranking officials participate in the cult's rituals, a blatant disregard for traditional Roman values. His personal conduct, marked by effeminate behavior and extravagant tastes, further alienated the Roman elite.
Beyond his religious fanaticism, Elagabalus was known for his lavish lifestyle. He spent exorbitant sums on personal luxuries, including exotic foods, rare animals, and lavish banquets. His sexual orientation and behavior were also a subject of much speculation and condemnation.
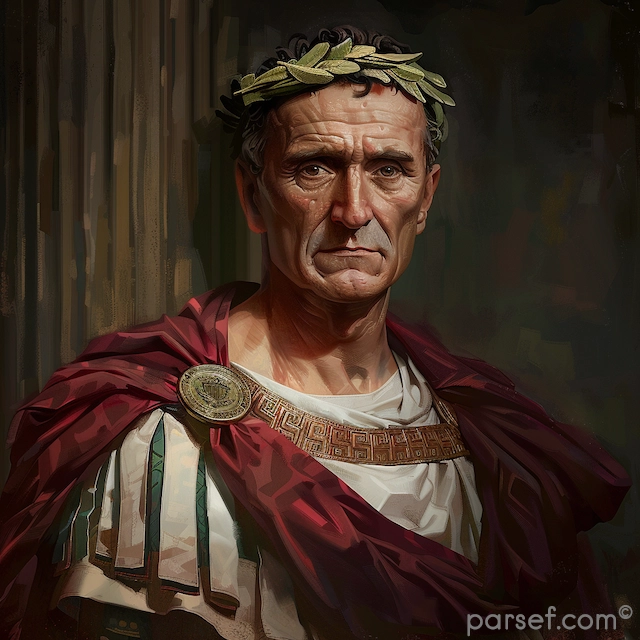
However, it is essential to approach the historical accounts of Elagabalus with caution. Much of the information about his reign comes from hostile sources, notably the historian Cassius Dio. These accounts, while colorful and dramatic, may exaggerate the emperor's excesses and eccentricities.
Ultimately, Elagabalus' reign proved to be short-lived. His unpopularity among the Senate and the Praetorian Guard grew, and he was assassinated in 222 AD. His cousin, Alexander Severus, succeeded him, ushering in a period of relative stability.
Elagabalus remains a complex and controversial figure. His reign was a period of radical experimentation, a departure from the traditional norms of Roman society. While his religious innovations were ultimately unsuccessful, they offer a fascinating glimpse into the religious and cultural landscape of the Roman Empire in the 3rd century.
Related Posts
Year of the Four Emperors: A Visual Timeline
📅 68 AD April: Galba, governor of Hispania Tarraconensis, and Vindex, governor of Gallia Lugdunensis, rebel against Emperor Nero.May: The Rhine legions defeat and kill Vindex in Gaul.June 8: The Senate declares Nero a public enemy.June 9: Nero commits suicide; Galba is recognized as emperor.November: Vitellius is appointed governor of Germania...
Read MoreNero: The Notorious Emperor Who Fiddled While Rome Burned
The name Nero is synonymous with tyranny, extravagance, and the infamous image of an emperor who, according to legend, played the fiddle while Rome was engulfed in flames. Nero's reign is a dark chapter in the history of the Roman Empire, marked by cruelty, decadence, and the disastrous Great Fire...
Read MoreThe Challenges and Blessings of Being a Christian in Modern Times
Christianity, born in a time of Roman rule and cultural upheaval, has always thrived amid paradox: power through humility, victory through suffering, life through death. In modern times—marked by rapid technological advancement, shifting moral landscapes, and growing religious pluralism—being a Christian is both profoundly challenging and richly rewarding. It calls...
Read MoreFrom Roman Thrones to Heavenly Crowns: The Emperor and the Rise of Catholicism
Once upon a time in the bustling heart of ancient Rome, emperors wore laurel wreaths and ruled sprawling empires with iron fists. Temples to Jupiter and Mars dotted the skyline, and gladiators clashed in the Colosseum under the approving gaze of the gods of Olympus. And yet, within this world...
Read MoreJerusalem Artisan Rosaries Handcrafted vs. Mass-Produced
In a world full of fast-made products, many believers are looking for devotional items that feel faithful, lasting, and true. Jerusalem Artisan Rosaries Handcrafted vs. Mass-Produced is more than a comparison—it’s a prayerful question: “What will help me (or someone I love) stay close to Jesus day after day?” This...
Read MoreSodom and Gomorrah: The Rise and Fall of Two Ancient Cities
Sodom and Gomorrah are two of the most infamous cities mentioned in ancient religious texts, notably the Bible. For centuries, they have symbolized divine judgment, moral depravity, and catastrophic destruction. Their story is told in the Book of Genesis, and echoes of their downfall reverberate through theology, archaeology, and mythology....
Read More